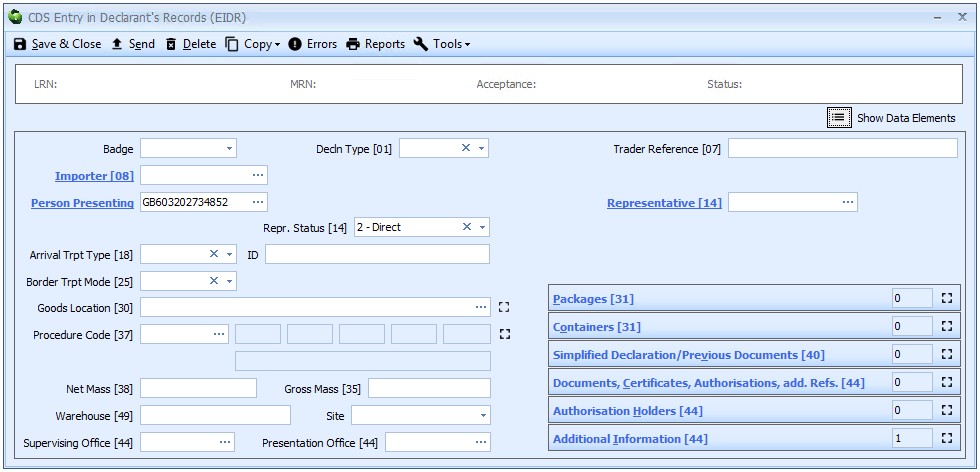
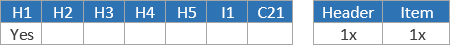
Completing Import CDS Declarations
The information below is derived essentially from the Import declaration completion guide for CDS and the UK Trade Tariff Volume 3 Customs Declaration Service Imports, both of which are available on gov.uk.
The information required to complete a declaration is listed on this page in SAD box number order, as that is the way it is laid out in the Sequoia CDS declaration forms.
The information in this resource is for information only. It is not intended to replace the law or the tariff guidance published by HMRC. However that information can be less than clear and concise.
The guidance on these pages therefore aims to simplify and clarify where possible the HMRC guidance into a more easily readable and accurate form. It also relates the legislative requirements to the process of actually making declarations in Sequoia.
All the information potentially required in a CDS import declaration is described in the sections below. The table of contents to the right lists these elements.
Most of the guidance on gov.uk - and below - still refers to 'the EU' and the 'member state' etc. Clearly we have left the EU and therefore this is no longer applicable and should refer to GB. However, the HMRC guidance - and in some cases the legislation - has as yet not been changed!
For each element there is a graphic (like the example below).
This graphic has 2 parts, each of which has a link to other, related information. Each part is described below.
This indicates when that data is required, depending on the declaration category. It also shows where, and how many times, that data can be declared at header and/or item level. Wherever that graphic appears, you can click on it to display a list of declaration categories. If this graphic is not present it means the data described is not a formal data element described in the legislation (e.g. Acceptance date).
Clicking the HMRC logo where it appears will take you to the relevant section of the HMRC Import declaration completion guide for CDS as it describes this specific data element. If the logo is not present it means the data described is not transmitted as part of the declaration (e.g. Badge).
Data Requirements
The data required in a CDS import declaration is listed below. It is listed in SAD box number order (where a box number is applicable).
Badge
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Although CDS does not relate badge codes to system access in the same way as CHIEF did, Sequoia uses the badge code as a mechanism for identifying the gateway through which the declaration will be sent.
You cannot therefore send a declaration in Sequoia until you have specified the badge code. This is the same for CHIEF declarations in Sequoia.
Once you have selected the badge code, Sequoia will generate an LRN for the declaration. The LRN will display in the summary panel at the top of the form.
The badge is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
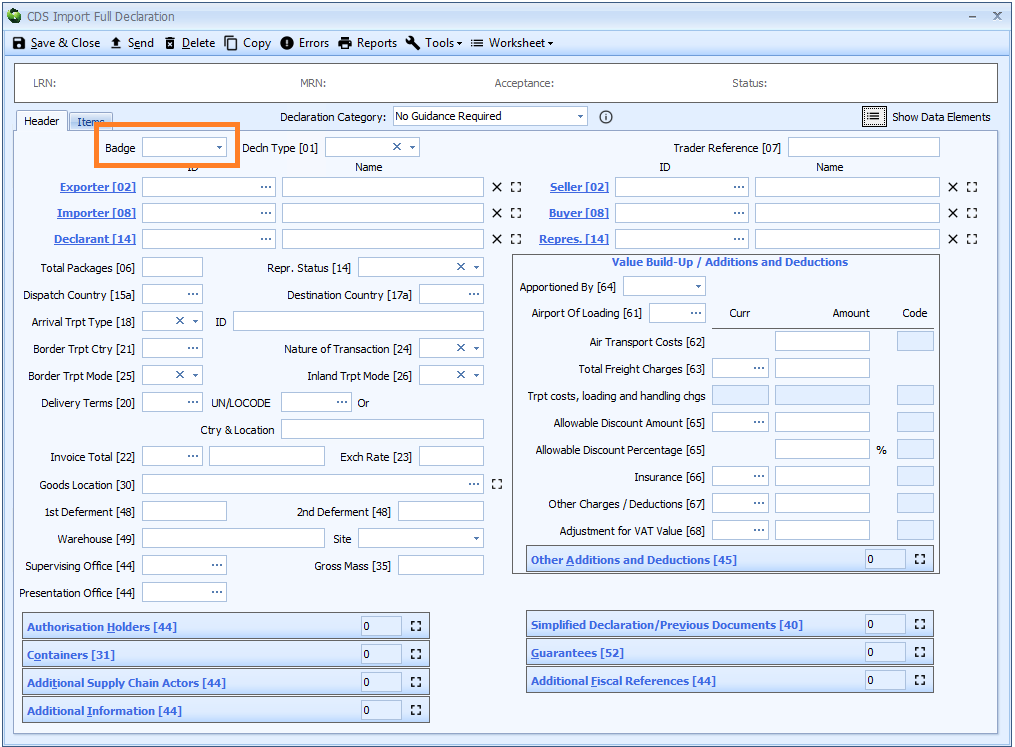
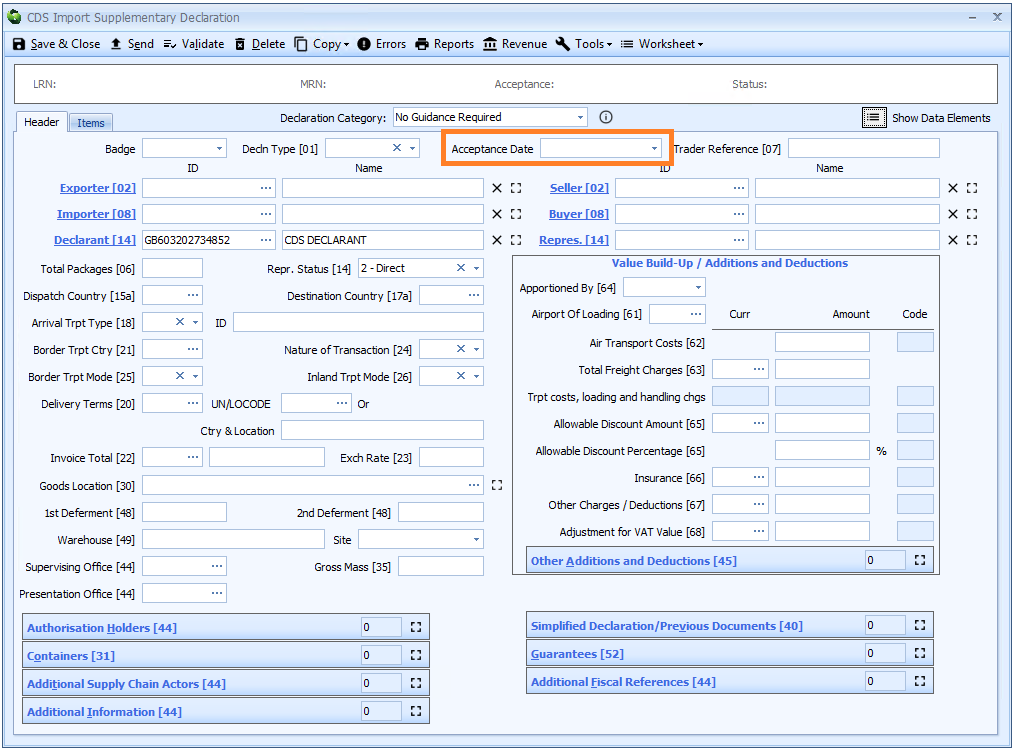
Acceptance Date
Declaring an acceptance (tax point) date is only required for a supplementary declaration.
You can type the date directly into the box - in the format dd/mm/yyyy - or click the ![]() icon to the right of the box to display a calendar (as shown below) from which you can select the date.
icon to the right of the box to display a calendar (as shown below) from which you can select the date.
If you are using the Sequoia customs warehousing module then, for a removal from the customs warehouse, this date will be automatically completed from the stock record.
Note that the time is also displayed in the box (in the format
hh:mm). You can specify a time if you wish but only the date is required and that is all that will be transmitted in the declaration.
The acceptance date is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
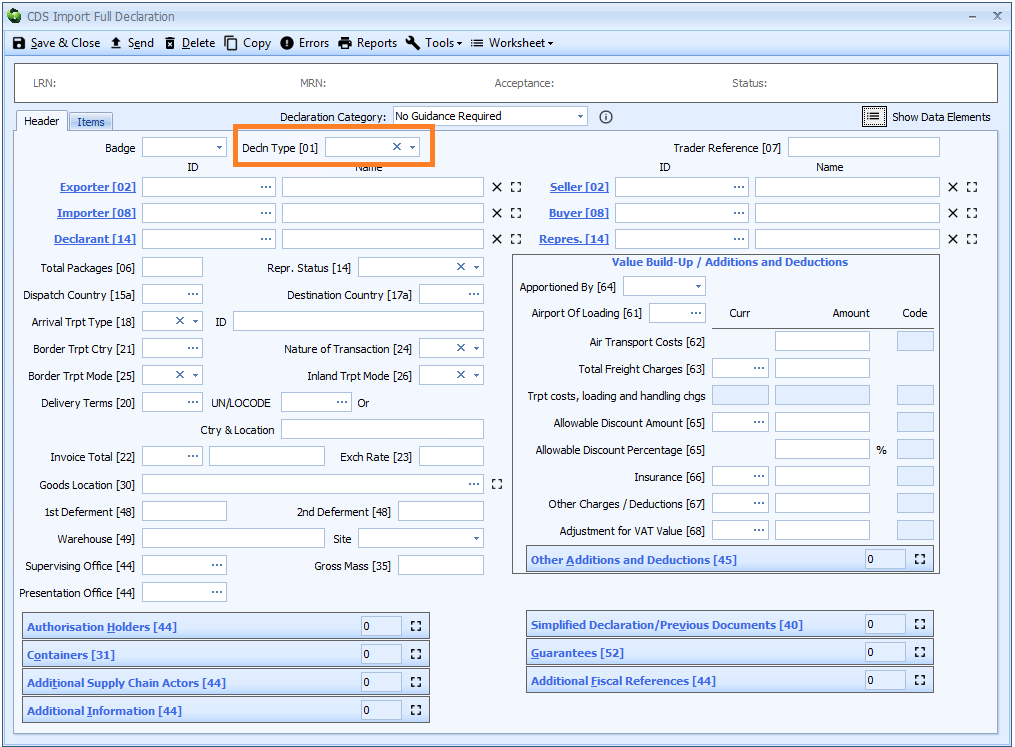
Box 01 - Declaration Type
DE 1/1 - Declaration type
DE 1/2 - Additional declaration type
In Sequoia this is combined into a single, 3 character code.
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Declaration Type is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
Declaration type has two components. The components are as follows:
Declaration type
DE 1/1 - Declaration type
The first component identifies the 'origin' of the goods and can be one of the following:
| Code | Type of declaration |
|---|---|
| IM | For trade with countries and territories situated outside of the Customs Territory of the Union. For placing non-Union goods under a customs procedure in the context of trade between member states. |
| CO | All the goods being declared are from a Special Fiscal Territory of the EU or a country with which the EU has formed a Customs Union. |
Additional declaration type
DE 1/2 - Additional declaration type
The second component (additional declaration type) indicates both the actual type of declaration (e.g. simplified) and if the goods have arrived or not at the goods location when the declaration is submitted.
| Code | Type of declaration | Goods arrived or not |
|---|---|---|
| A | Standard (full) customs declaration | Goods arrived |
| B | Simplified declaration on an occasional basis | Goods arrived |
| C | Simplified declaration with regular use (pre-authorised) | Goods arrived |
| D | Standard (full) customs declaration | Goods not arrived |
| E | Simplified declaration on an occasional basis | Goods not arrived |
| F | Simplified declaration with regular use (pre-authorised) | Goods not arrived |
| J | C21 | Goods arrived |
| K | C21 | Goods not arrived |
| Y | Supplementary declaration covered by types C and F | Goods arrived |
| Z | Supplementary declarations for Entry in Declarants Records | Goods arrived |
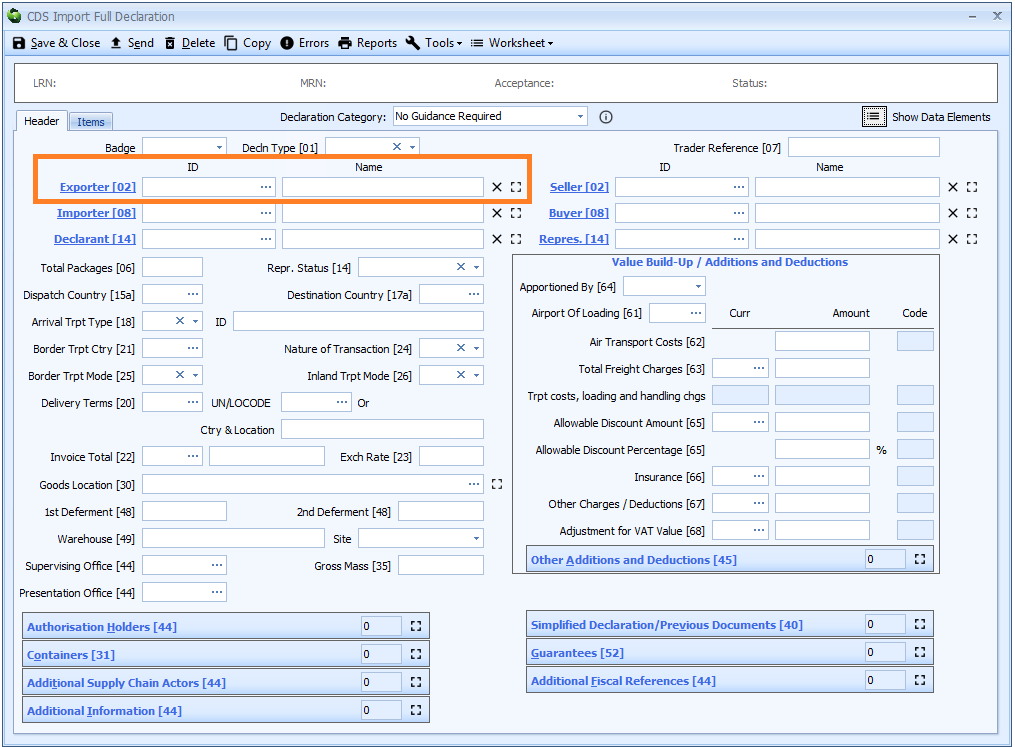
Box 02 - Exporter and Seller
Exporter - and in certain circumstances Seller - replace Consignor in box 02.
Exporter
DE 3/1 - Exporter name and address
DE 3/2 - Exporter EORI number
If you are creating a declaration from a job then the exporter will automatically be completed with the consignor specified on the job record.
Type in all or part of their shortcode, EORI number or name into either the ID or name box.
You can also enter ? - a question mark - into the ID or Name box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required party.
For more information, see how party controls work in Sequoia.
Exporter is declared on the header tab of the declaration form if it is the same for all the goods on the declaration, otherwise it must be declared for each item on the item tab.
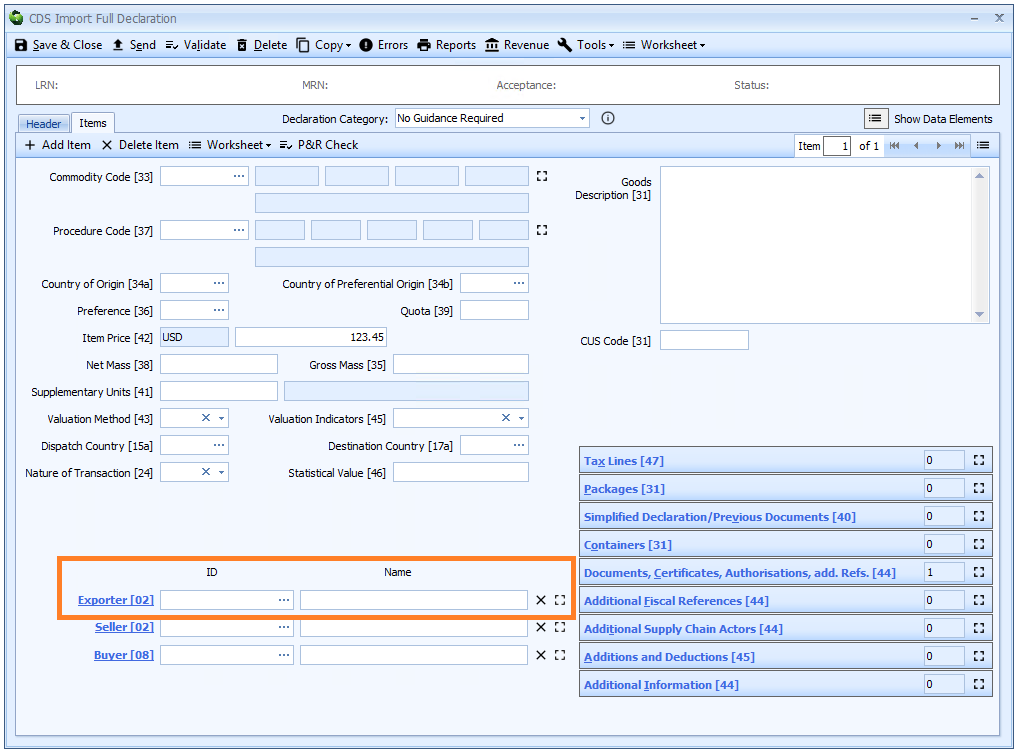
If there is only one exporter for all the goods then it is declared at header level.
Otherwise:
00200must be entered in each of the Name, Street, City and Postcode fields at header level- The Exporter's details must be declared for each item.
If the exporter has an EORI number then that should be declared. Otherwise the full name and address (street, city, postcode and country code) is required.
Seller
DE 3/24 - Seller name and address
DE 3/25 - Seller identification number
The seller is only required for a declaration for release for free circulation or a declaration for end use and only if different from the exporter.
To specify a seller you can type in all or part of their shortcode, EORI number or name into either the ID or name box. You can also enter ? - a question mark - into the ID or Name box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required party.
For more information, see how party controls work in Sequoia.
Seller is declared on the header tab of the declaration form if it is the same for all the goods on the declaration, otherwise it must be declared for each item on the item tab.
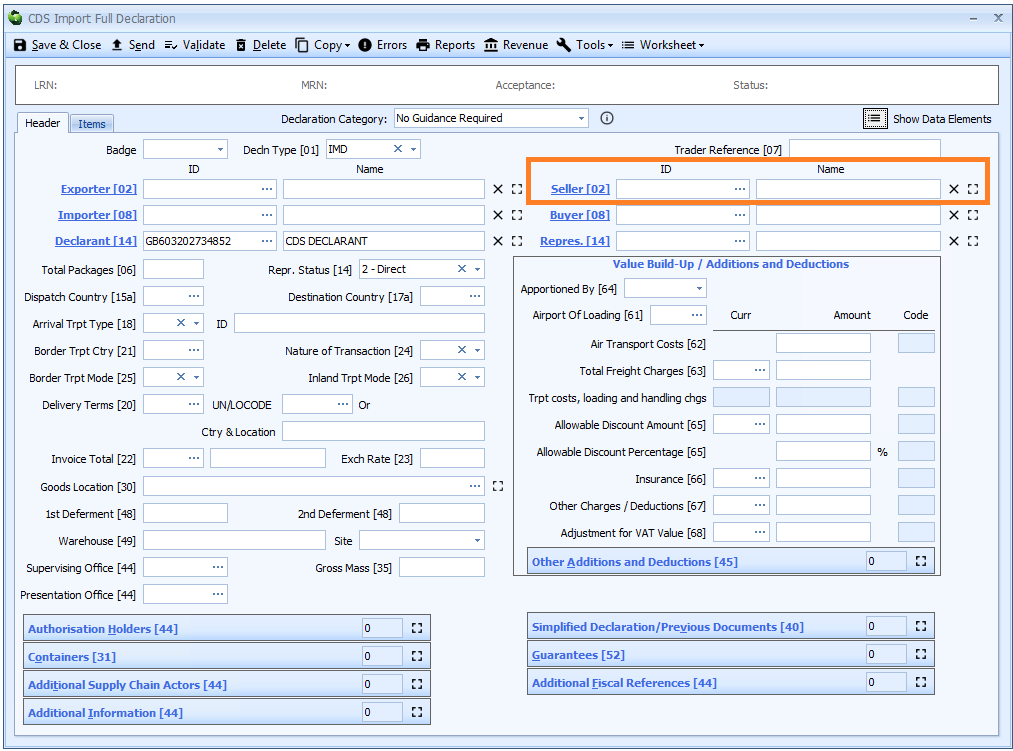
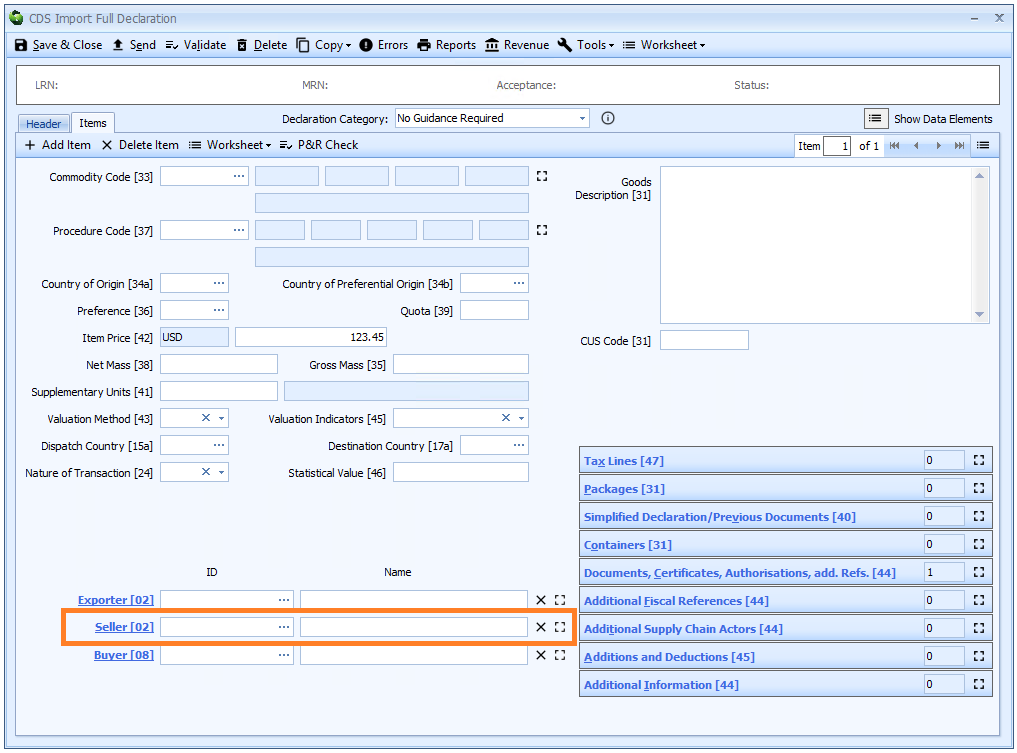
If the seller has an EORI number then that should be declared. Otherwise the full name and address (street, city, postcode and country code) is required.
As the exporter is defined as "the last seller of the goods prior to their importation into the Union" and the import declaration is the importation then it is hard to imagine a circumstance in which the seller could be a different entity on an import declaration.
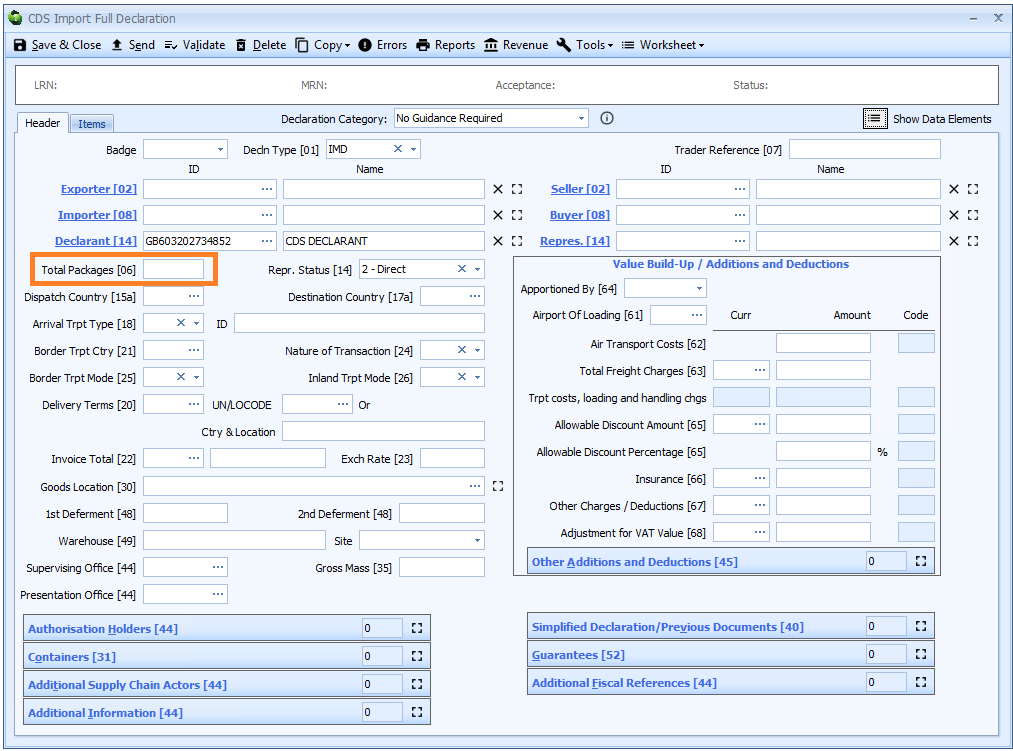
Box 06 - Total Packages
DE 6/18 - Total packages
Enter the total number of packages making up the consignment covered by the declaration.
If the declaration is inventory linked then the total packages must be the same as that recorded on the inventory record. If you are creating the declaration from a job, Sequoia will automatically complete this from the inventory or shipment record.
Total packages is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
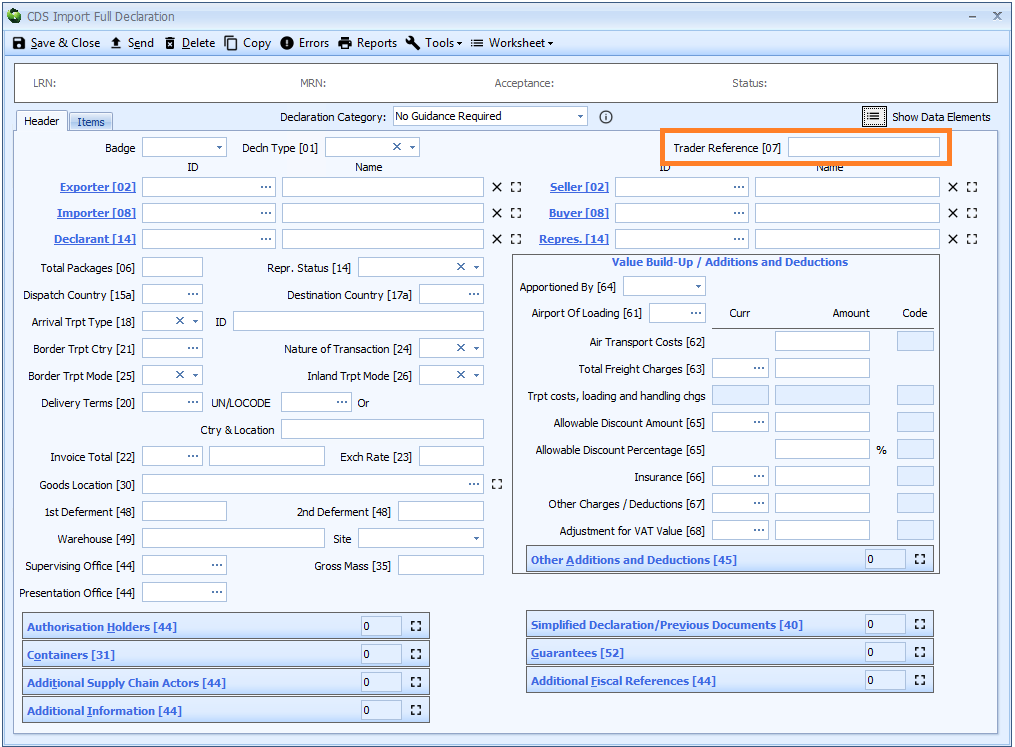
Box 07 - Trader Reference
DE 2/4 - Reference number/UCR
This is an optional trader specified reference number. Although described in the legislation as a UCR, it should not be confused with the DUCR (Declaration UCR) of which it forms a part.
Although specified in the legislation as being up to 35 characters, in Sequoia it is restricted to 19 characters (for both CDS and CHIEF declarations) as it is used as part of the Declaration UCR.
If the declaration is created from a job then this trader reference will automatically contain the job reference.
Trader Reference is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
Box 08 - Importer and Buyer
Importer - and in certain circumstances Buyer - replace Consignee in box 08.
Importer
DE 3/15 - Importer name and address
DE 3/16 - Importer identification number
If you are creating a declaration from a job then the importer will automatically be completed with the consignee specified on the job record.
To specify an importer you can type in all or part of their shortcode, EORI number or name into either the ID or Name box.
You can also enter ? - a question mark - into the ID or Name box to display a lookup dialog from
which you can select the required party.
For more information, see how party controls work in Sequoia.
The importer is defined as "the party who makes, or on whose behalf an import declaration is made".
Importer is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
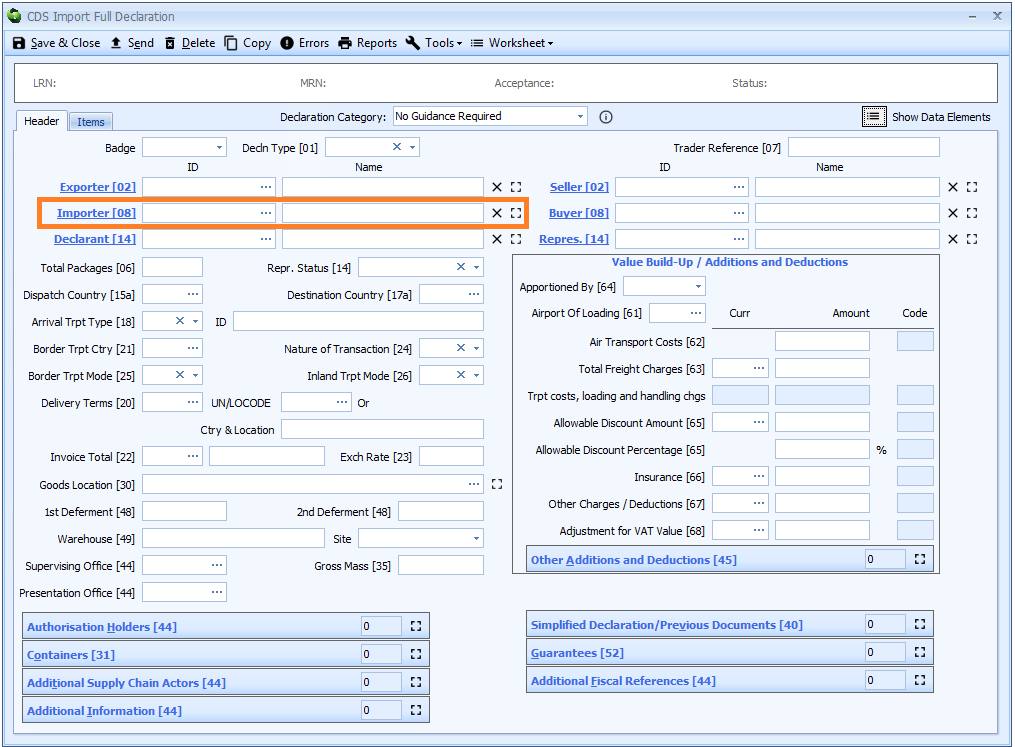
If the importer has an EORI number then that should be declared. Otherwise the full name and address (street, city, postcode and country code) is required. It is not considered to be an error if both the EORI number and name and address are declared.
For commercial importations an EORI number must be used unless a specific legal exemption applies. This applies to all commercial imports including ‘one off’ consignments.
An import VAT certificate C79 will only be issued when a recognised VAT registered importer’s EORI number is declared.
For non EU traders who do not require an EORI number, under (Article 5 EU Reg No. 2015/2446):
00500in box 44 - Additional Information at item level00500as the Importer’s name, prefaced by the non-EU country code of the importer followed by their name- their address as normal.
For (LVBI) bulked low value declarations using box 37 - Additional Procedure Code 1LV or 2LV, enter the EORI number of the LVBI authorisation holder. See Appendix 2 - Additional procedure codes.
When goods are being entered for a private customs warehouse, the identity of the approved warehouse keeper is required as the importer.
When goods are declared for removal from free zones, other than for export, enter the identity of the person removing the goods from the free zone or placing them in free circulation.
Where the goods are sold in warehouse as a retail sale, the depositor of the goods should be declared as the importer. The buyer of the goods under the retail sale should be declared as the Buyer.
Buyer
DE 3/26 - Buyer name and address
DE 3/27 - Buyer identification number
The buyer is only required for a declaration for release for free circulation or a declaration for end use and only if different from the importer.
To specify a buyer you can type in all or part of their shortcode, EORI number or name into either the ID or Name box.
You can also enter ? - a question mark - into the ID or Name box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required party.
For more information, see how party controls work in Sequoia.
The buyer is defined as "the last known entity to whom the goods are sold or agreed to be sold. If the goods are to be imported otherwise than in pursuance of a purchase, the details of the owner of the goods shall be provided"
Buyer is declared on the header tab of the declaration form if it is the same for all the goods on the declaration, otherwise it must be declared for each item on the item tab.
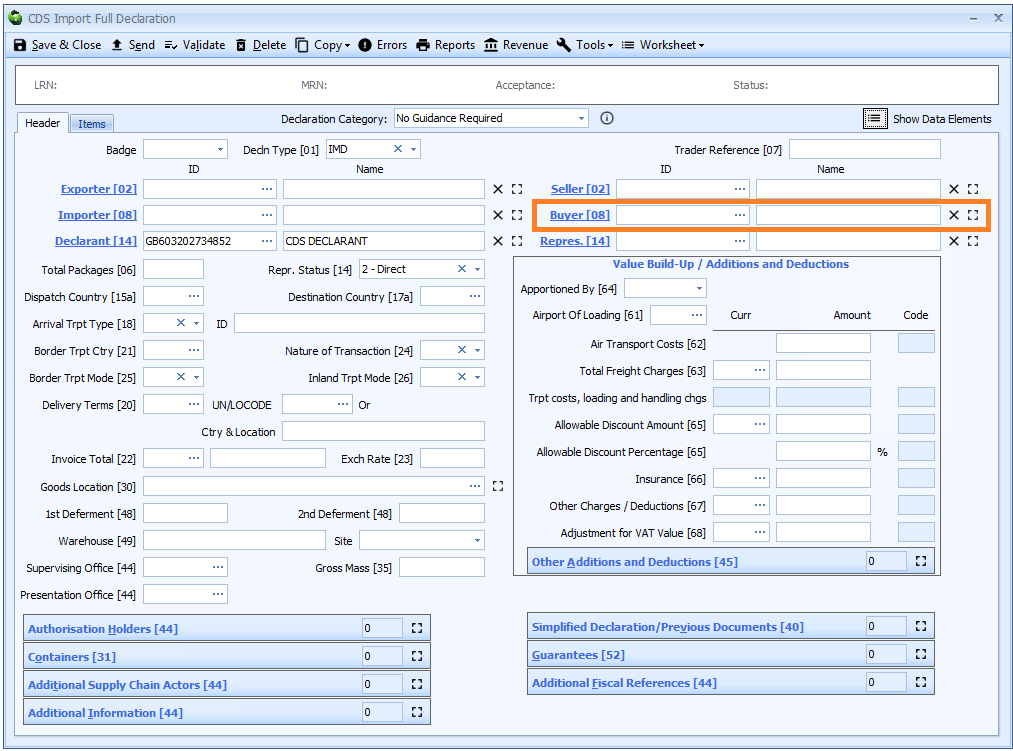
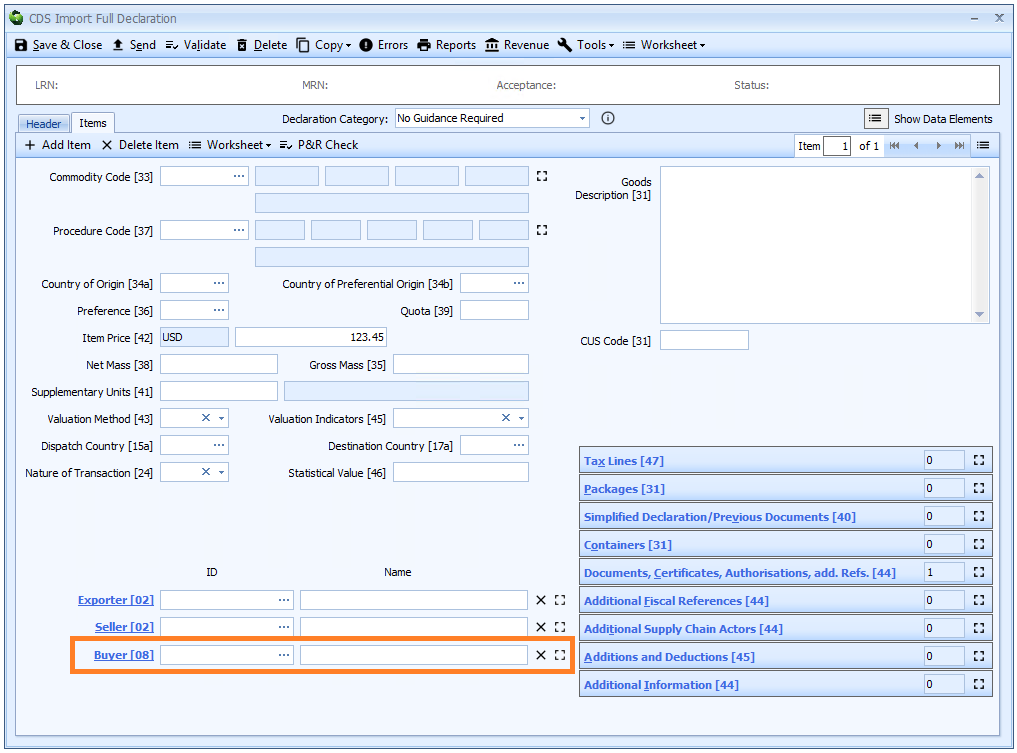
If the buyer has an EORI number then that should be declared. Otherwise the full name and address (street, city, postcode and country code) is required.
Box 14 - Declarant and Representative
Declarant - and in certain circumstances Representative - replace Declarant in box 14.
Declarant
DE 3/17 - Declarant name and address
DE 3/18 - Declarant identification number
Declarant is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
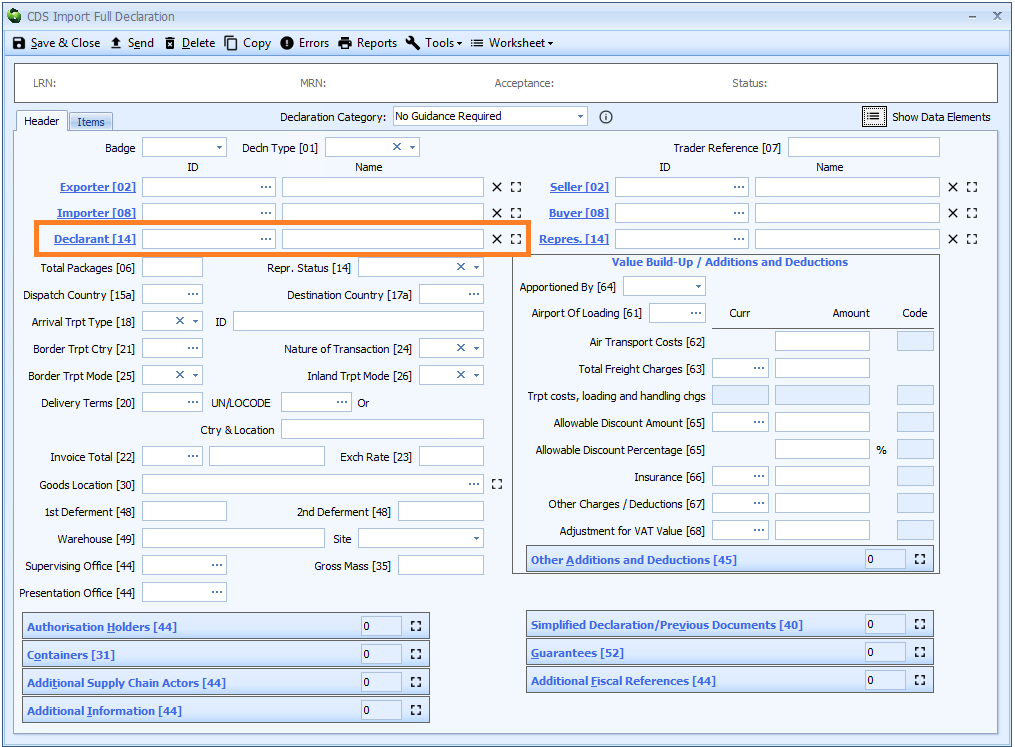
The declarant will automatically be completed if you have a CRM record configured as your default declarant. See how to configure a default declarant in Sequoia for more details.
To specify the declarant you can type in all or part of their shortcode, EORI number or name into either the ID or Name box.
You can also enter ? - a question mark - into the ID or Name box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required party.
For more information, see how party controls work in Sequoia.
Completing a declaration as a sub-agent
If you are completing a declaration on behalf of another agent, then your details should be declared as the declarant (DE 3/17 + 3/18) and their details should be declared as the Representative (DE 3/19 + 3/20).
Representative status (DE 3/21) should reflect the representation status agreed between the importer and the agent for whom you are submitting the declaration.
Representative
DE 3/19 - Representative name and address
DE 3/20 - Representative identification number
Representative is only required where that party differs from the declarant, for example where the Representative contracts with a sub-agent to submit the customs declaration.
Completing a declaration as a sub-agent
If you are completing a declaration on behalf of another agent, then your details should be declared as the declarant (DE 3/17 + 3/18) and their details should be declared as the Representative (DE 3/19 + 3/20).
Representative status (DE 3/21) should reflect the representation status agreed between the importer and the agent for whom you are submitting the declaration.
Representative is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
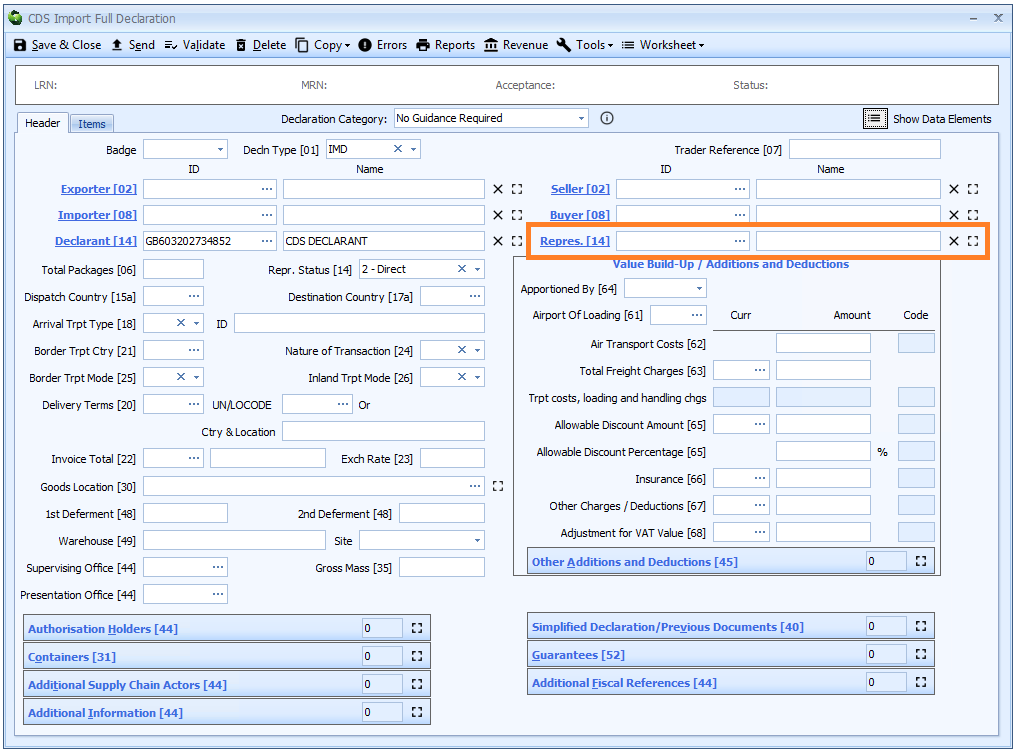
If the representative has an EORI number then that should be declared. Otherwise the full name and address (street, city, postcode and country code) is required.
Representative Status
DE 3/21 - Representative status code
Representative Status is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
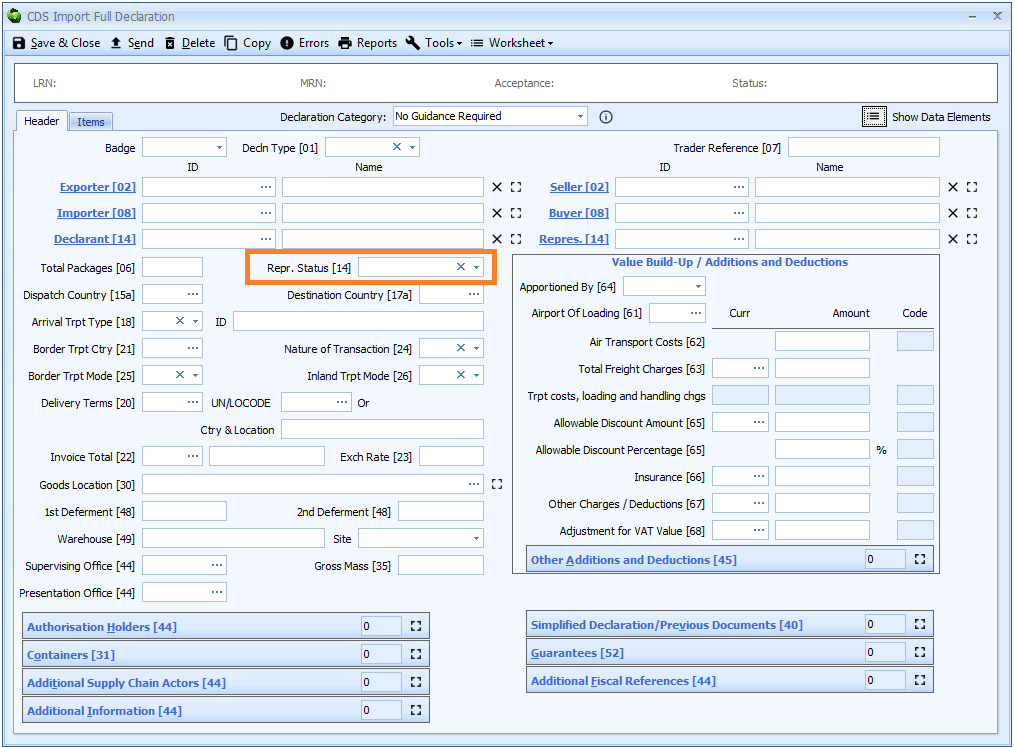
You can type the single digit code (see below) directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box..
icon to the right of the box..
The legislation permits customs representatives to be appointed to act on another person’s behalf. This representation may be:
-
2- Direct; the representative acts in the name and of behalf of the other person. -
3- Indirect; the representative acts in their own name but on behalf of another person.
Completing a declaration as a sub-agent
If you are completing a declaration on behalf of another agent, Representative status should reflect the representation status agreed between the importer and the agent for whom you are submitting the declaration.
Box 15a - Dispatch Country
DE 5/14 - Country of dispatch/export code
If Dispatch country is the same for all the goods on the declaration then it should be entered at header level. Otherwise it must be declared for each item.
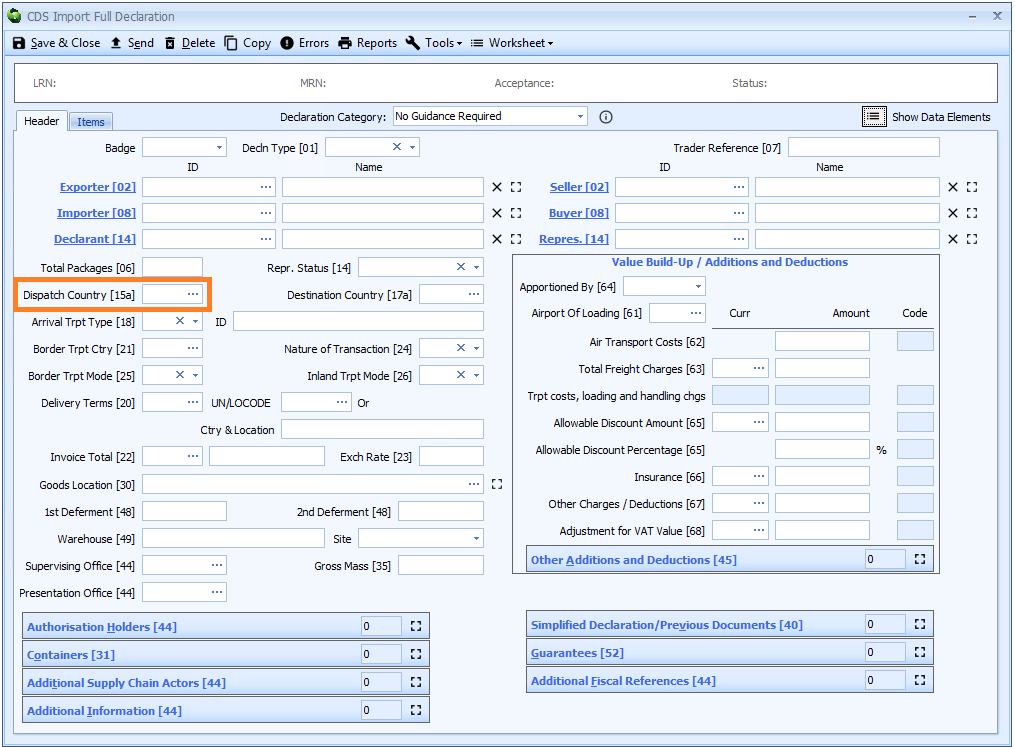
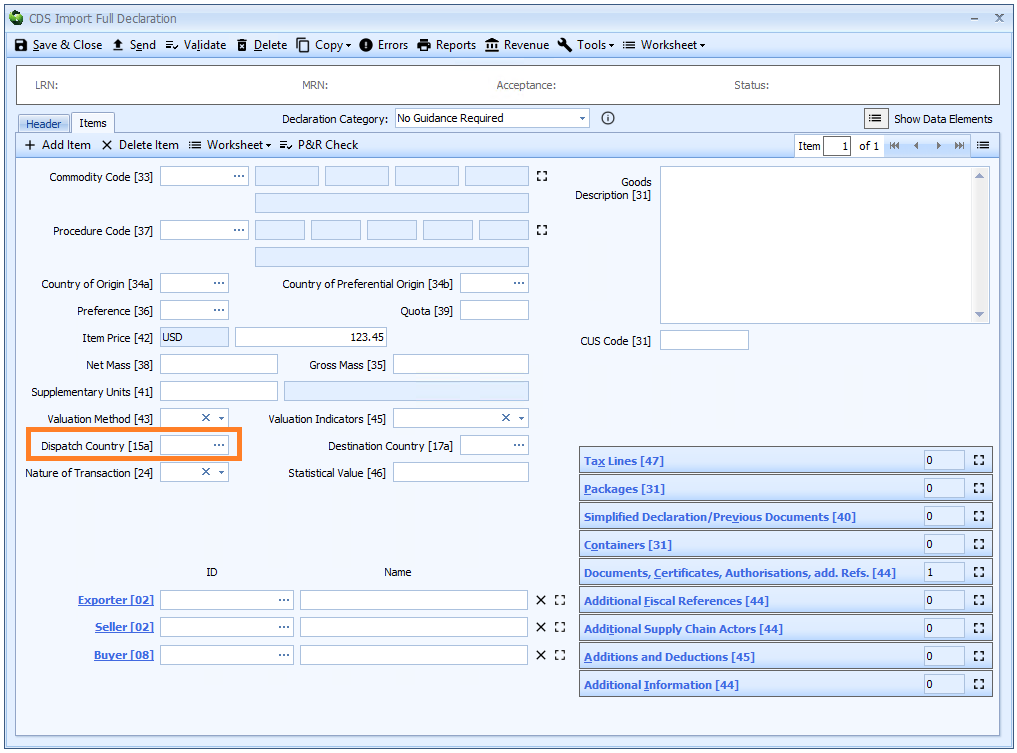
Enter the relevant code for the third country or territory from which the goods were initially dispatched to the UK.
However, where there has been a:
- stoppage (including consolidation), or;
- legal action taken in respect of the goods in an intermediate country, (for example, a non-EU country undertook an inspection which caused them to remain in that country for a longer period than would normally have been the case), or:
-
commercial transactions en-route (for example, a change of ownership in an intermediate country)
then you should enter the country code for the last intermediate country; for example, the non-EU country where the goods were last located before arrival in the UK where the change took place.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required country code.
A list of country codes can also be found [here].
Box 17a - Destination Country
DE 5/8 - Country of destination code
If Destination country is the same for all the goods on the declaration then it should be entered at header level. Otherwise it must be declared for each item.
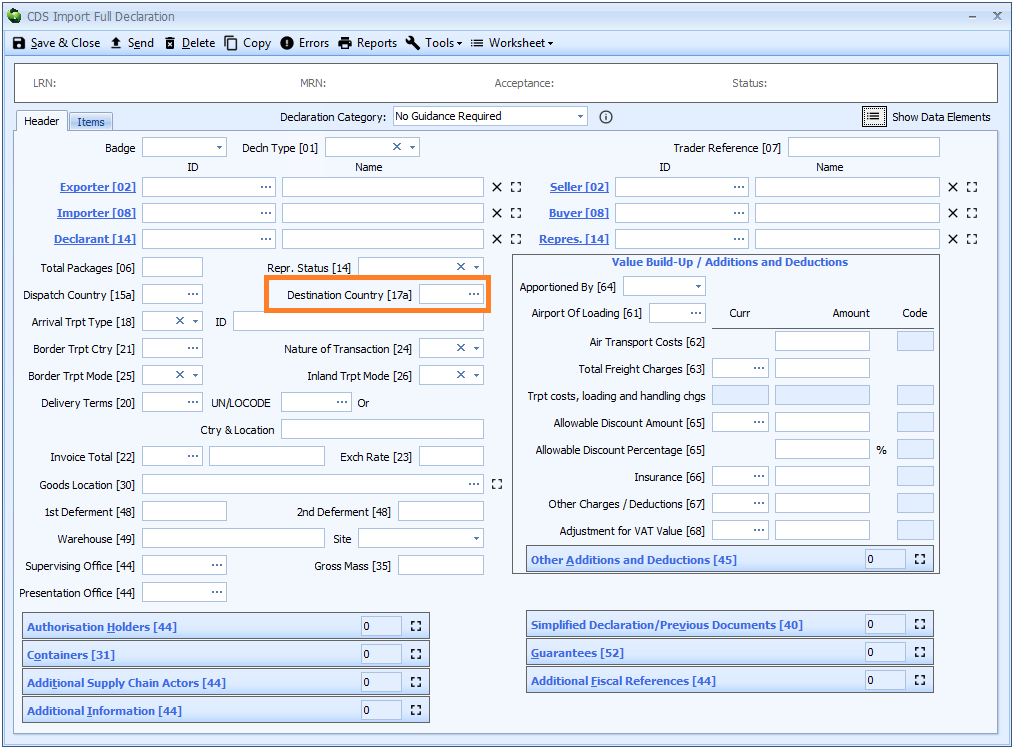
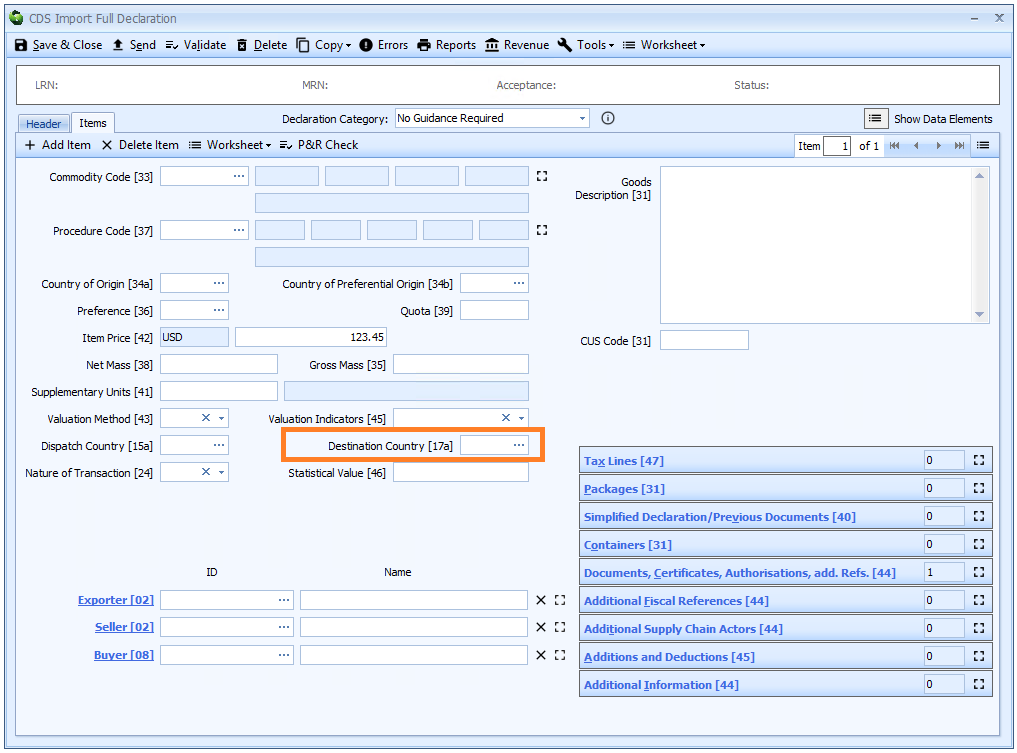
Note that the legislation - and the guidance on gov.uk - still states that this should/must be an EU member state! Clearly, since we have left the EU, this is no longer the case.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required country code.
A list of country codes can also be found [here].
Box 18 - Transport ID on Arrival
DE 7/9 - Identity of means of transport on arrival
Transport ID on Arrival is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
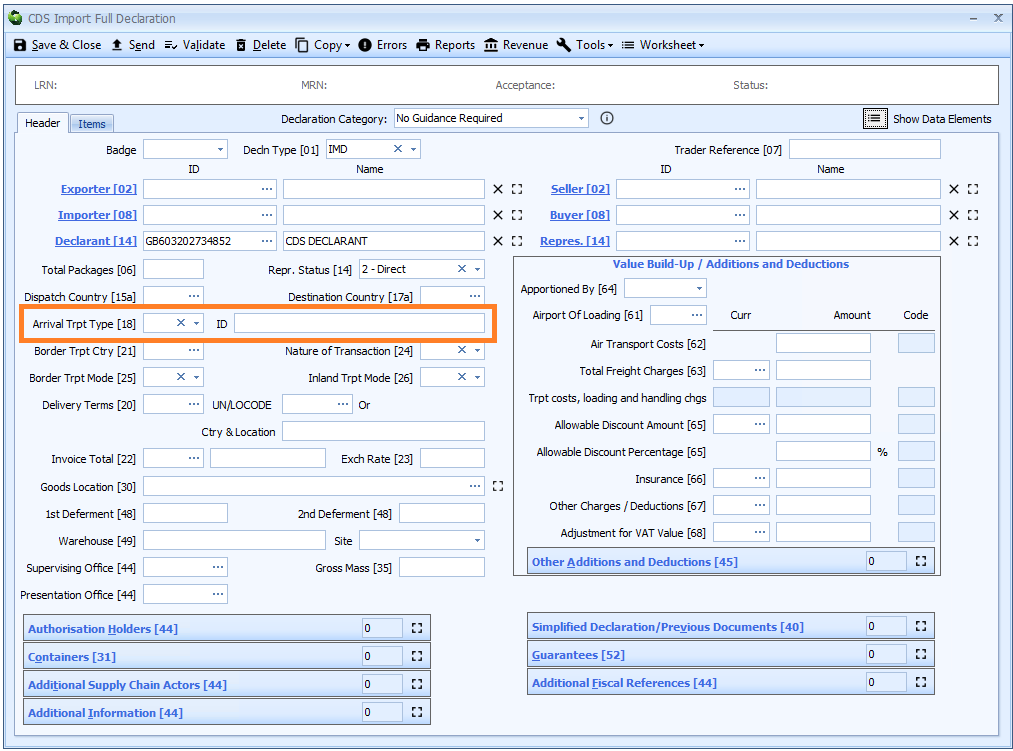
This has two components as follows:
Transport type
This is a two digit code identifying the type of transport (that the ID relates to).
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Below is a list of valid transport type codes.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 10 | IMO ship identification number |
| 11 | Name of the sea-going vessel |
| 20 | Wagon number |
| 30 | Registration number of the road vehicle |
| 40 | IATA flight number |
| 41 | Registration number of the aircraft |
| 80 | European Vessel Identification Number (ENI code) |
| 81 | Name of the inland waterways vessel |
Transport ID
Enter the identity of the means of transport on which the goods are directly loaded at the time of presentation at the customs office of import.
If a tractor and trailer with different registration numbers are used, enter the registration number of both the tractor and the trailer.
| Means of transport | Method of identification |
|---|---|
| Sea and inland waterway transport | Name of vessel |
| Air transport | Number and date of flight. Where there is no flight number, enter the aircraft’s registration number. |
| Road transport | Vehicle registration number |
| Rail transport | Wagon number |
The identity is not required if the mode of transport at the border (box 25) is entered as 5 (Postal Consignments) or 7 (Fixed Transport Installation).
Box 19 - Container
DE 7/2 - Country of destination code
This indicates whether the goods "will be in a shipping container when crossing the external frontier of the Union". That is represented as containerised 1 or not 0.
Sequoia does not require you to fill this in. Rather it is implied by the presence or absence of container numbers in box 31 at either header or item level or both.
Box 20 - Delivery Terms
DE 4/1 - Delivery terms
Delivery terms (the terms of the commercial contract) are required for declarations using Valuation Method 1 - the transaction value of the goods.
Delivery terms are declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
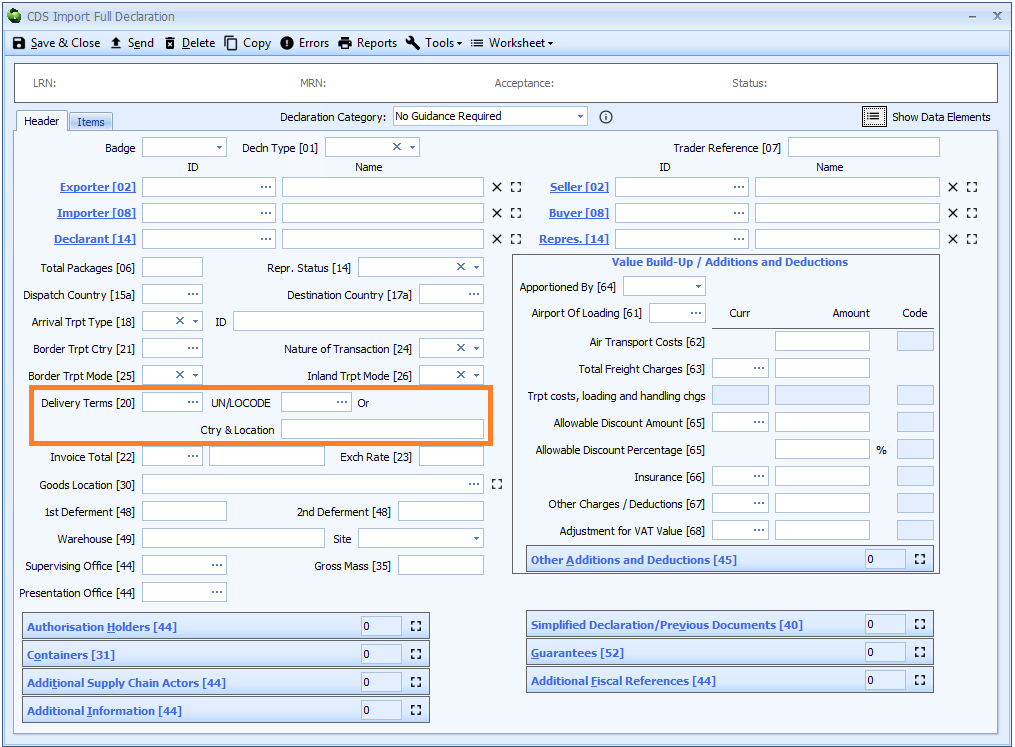
The delivery terms consist of two components as follows:
INCOTERM Code
You can enter the code into the box - labelled 'Delivery Terms [20]' - or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of allowable INCOTERM codes can be found here
Location
Enter the location up to which the INCOTERM applies.
The UN/LOCODE must be used where an appropriate code exists. You can enter the code into the 'UN/LOCODE' box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of allowable UN/LOCODEs can also be found here.
If no UN/LOCODE exists for the location, then enter a plain language description for the location in the 'Ctry & Location' box. This should be entered as the country code followed by the place name - e.g. GBCanewdon.
Delivery terms are only required on a simplified declaration where a claim to a tariff quota is being made on the simplified declaration.
Delivery terms must be completed for importations to Inward Processing when the declarant opts to use the Article 86(3) customs debt rules as laid down in the UCC.
When
E01orE02are being declared in box 37 - additional procedure codes, you should leave delivery terms blank.
Box 21 - Border Transport Country
DE 7/15 - Identity of active means of transport crossing the border
Border transport nationality (country) is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required country code.
Enter the nationality of the active means of transport crossing the Union’s external frontier, except:
- in the case of ships or aircraft registered in the colonies or dependencies of a foreign country, enter the nationality of that country, ;
- in the case of ships or aircraft registered in the UK’s dependent territories, enter the nationality of that territory.
A list of country codes can also be found [here].
Box 22 - Invoice Total
DE 4/10 - Invoice currency
DE4/11 - Total amount invoiced
The invoice total is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
Invoice total consists of both the currency code and amount. If you enter it then you must enter both currency code and amount, and it must correspond to the total of the item price values entered in box 42 - item price.
You can enter the currency code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
The invoice amount can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 2 digits may be after the decimal point. I.e. if you have 2 decimal places, you can only have up to 14 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
A list of currency codes can also be found [here].
Box 23 - Exchange Rate
DE4/15 - Exchange rate
In normal circumstances, you do not need to specify an exchange rate. CDS will convert any foreign currency amounts declared in a declaration using published rates of exchange.
However, if the goods being declared are subject to a rate of exchange fixed in advance by a contract between the parties concerned, you must declare that exchange rate.
If you do declare an exchange rate then the Invoice Total and/or the Item Price for each item must be declared in GBP and a copy of the worksheet or valuation declaration, showing how the conversion was made, must be held and made available to Customs on request.
The Exchange Rate is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
In those circumstances, document code 9WKS must also be declared in box 44 - Documents, Certificates, Authorisations and Additional References.
The exchange rate can be up to 12 digits, of which up to 5 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 5 decimal places, you can only have up to 7 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 12 digits before the decimal point.
Box 24 - Nature of Transaction
DE8/5 - Nature of Transaction
Nature of transaction is declared on the header tab of the declaration form where it is the same for all items. Otherwise it is declared on the item tab.
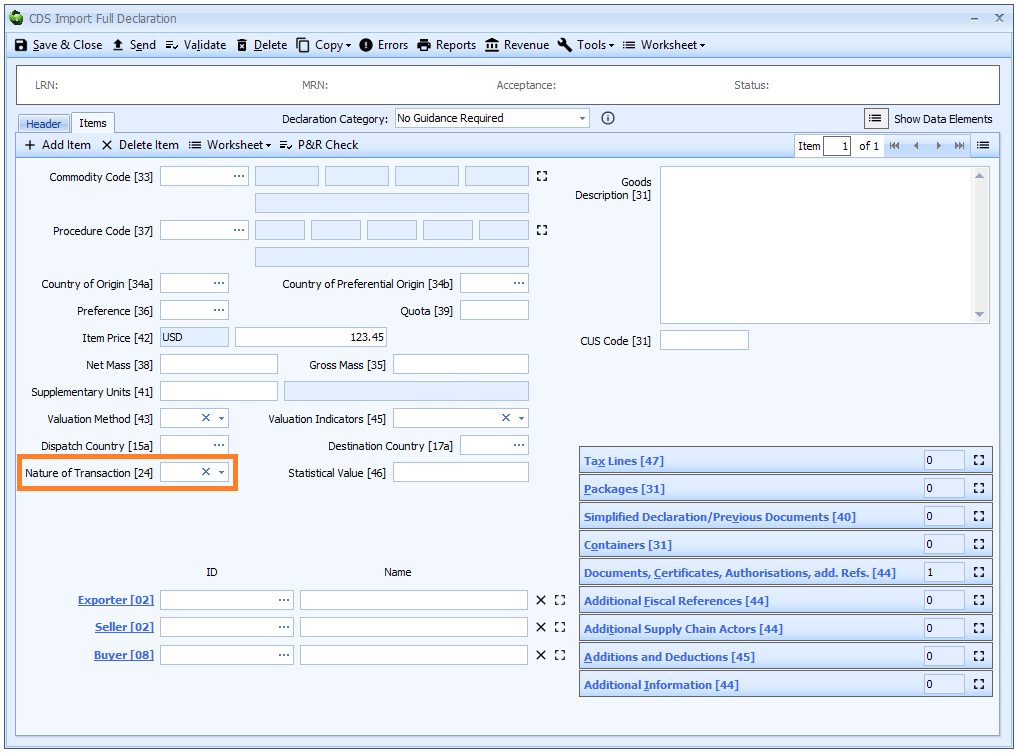
Enter the relevant code for type of transaction from the table below. The first digit is mandatory. The second digit - if there is one - is optional.
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
This dropdown in Sequoia only lists the first digit codes. You can type a 2 digit code directly into the box.
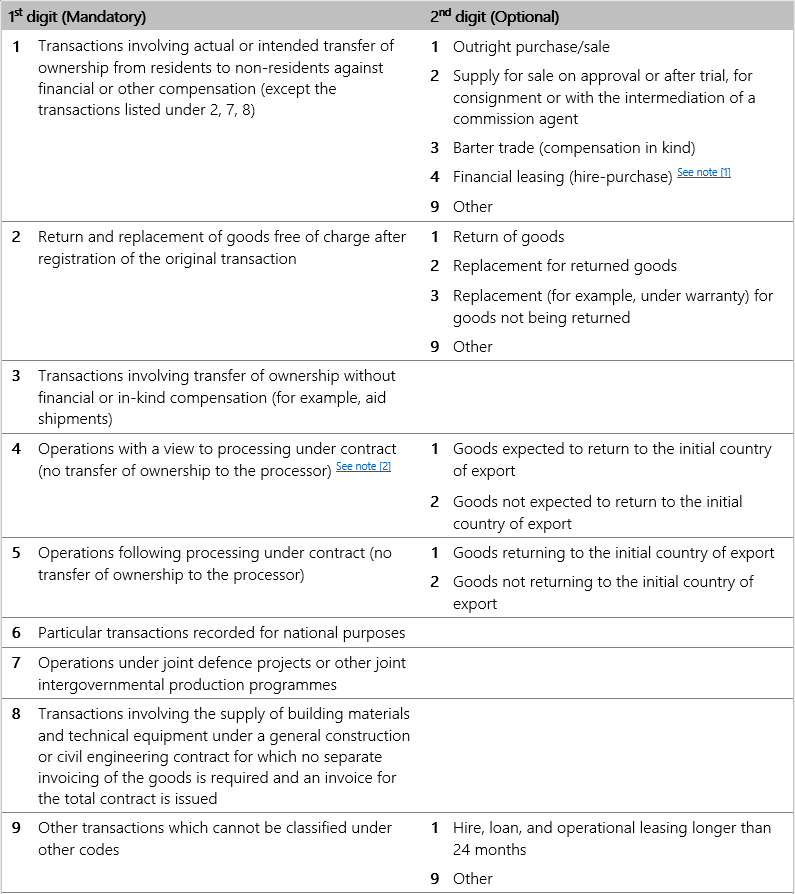
Notes
- Financial leasing covers operations where the lease instalments are calculated in such a way as to cover all or virtually all the value of the goods. The risks and rewards of ownership are transferred to the lessee. At the end of the contract the lessee becomes the legal owner of the goods.
- Processing covers operations (transformation, construction, assembling, enhancement, renovation …) with the objective of producing a new or really improved item. This does not necessarily involve a change in the product classification. Processing activities on a processor’s own account are not covered by this item and should be registered under item 1 of column A.
Box 25 - Border Transport Mode
DE7/4 - Mode of transport at the border
Border transport mode is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
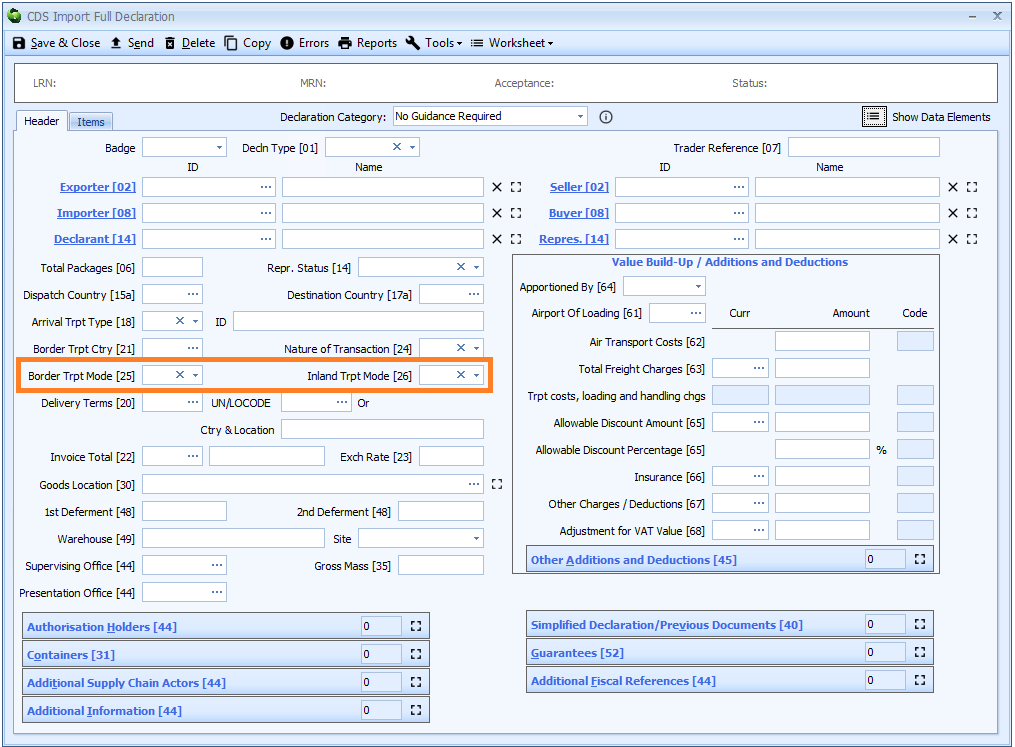
Enter the relevant code from the list below for the mode of transport used to arrive at the EU external border.
You can type the code (see below) directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
| Mode of transport | Mode Code |
|---|---|
| Maritime (Sea) transport | 1 |
| Rail transport | 2 |
| Road transport | 3 |
| Air transport | 4 |
| Postal (Mail) consignment* | 5 |
| Fixed transport installations | 7 |
| Inland waterway transport | 8 |
| Mode unknown - for example, own propulsion | 9 |
* Code 5 should only be used for goods handled by an authorised postal operator which is governed by the Universal Postal Union (for example, Royal Mail Group). The ‘actual’ mode of transport should be used for all other goods.
Box 26 - Inland Transport Mode
DE7/5 - Inland mode of transport
Inland transport mode is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.

Enter the relevant code from the list below when import formalities are carried out away from the point of entry into the EU.
You can type the code (see below) directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Completion is not required for entry into a customs warehouse or removals from a free zone.
| Mode of transport | Mode Code |
|---|---|
| Maritime (Sea) transport | 1 |
| Rail transport | 2 |
| Road transport | 3 |
| Air transport | 4 |
| Postal (Mail) consignment* | 5 |
| Fixed transport installations | 7 |
| Inland waterway transport | 8 |
| Mode unknown - for example, own propulsion | 9 |
* Code 5 should only be used for goods handled by an authorised postal operator which is governed by the Universal Postal Union (for example, Royal Mail Group). The ‘actual’ mode of transport should be used for all other goods.
Box 30 - Goods Location
DE5/23 - Location of goods
Goods location codes are a lot more complicated than those used in CHIEF declarations. This is essentially due to the definition in the legislation.
They are also not particularly easy to find on gov.uk due to them being listed in 14 different appendices! You can see those appendices here.
Luckily, Sequoia allows you to look up and choose from a list of your added location codes. Please refer to this guide to adding frequently used locations. For inventory-linked declarations, the correct location code will be automatically completed for you if configured, again refer to the guide.
The HMRC Import declaration completion guide for CDS currently does not require the goods location on a C21 declaration. As a C21 is essentially an inventory release it is hard to see why this is the case.
The location of goods is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
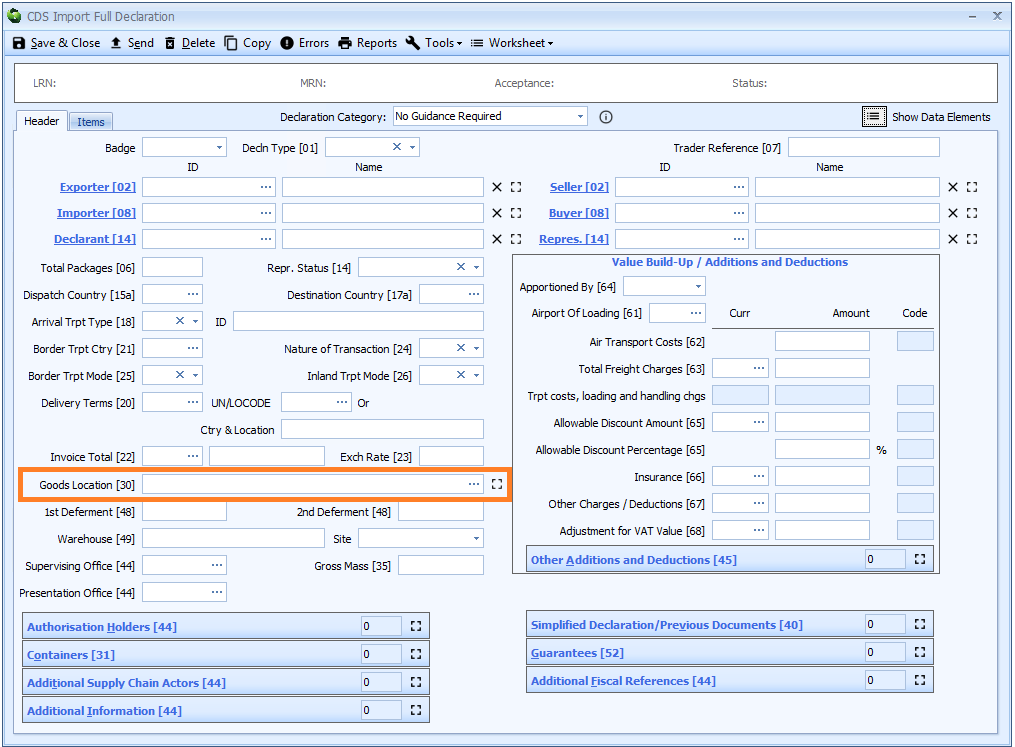
Should you need to, you can click on the ![]() icon to expand the control as necessary.
icon to expand the control as necessary.
Click the ![]() icon (to the top right of the control) to collapse the control again.
icon (to the top right of the control) to collapse the control again.
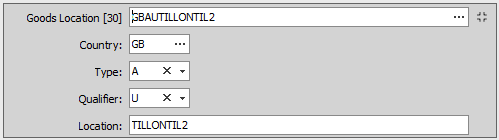
Each goods location code is broken down into 4 components. These 4 components are displayed on the expanded control.
Each part (country, type and qualifier) can be searched and listed individually using the lookup and dropdown controls. You can also search for a full code by entering ? - a question mark - into the box labelled 'Goods Location [30]' at the top of the control.
The components are as follows:
Country code
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required country code.
Enter GB unless:
- the declaration relates to goods being removed from a warehouse in another member state in which case this component should be completed with the appropriate code, followed by the Warehouse ID
- the goods are being declared to the UK under SASP arrangements for goods released to the customs procedure in another member state. In these situations the UN/LOCODE for the port or airport in the other member state should be declared.
Type of location
You can type the code (see below) directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
The type of location is indicated using a single character code as follows:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Frontier or Frontier linked locations such as Airports, ITSFs etc. |
| B | Inland locations such as customs warehouses. |
| C | Certificate of Agreement Airfields. |
| D | Other types of locations such as pipelines, continental shelf, wind farms, etc. |
Qualifier code
You can type the code (see below) directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Although there are seven codes defined in the legislation, only 2 of these are being used in the UK, as follows:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| U | The goods location is identified using a UN/LOCODE |
| Y | The goods location is identified by an authorisation number. |
Location Code and Additional Qualifier
This is technically made up of two parts:
Location code
This is a three-character UN/LOCODE (not including the country code)
Additional qualifier
This is a unique code assigned to each location to identify the specific location concerned, for example, a specific ITSF shed. It also generally includes the old CHIEF port code.
Total Net Mass and Total Gross Mass
Completion of these fields will allow the item level Net and Gross Mass to be automatically apportioned based on the ratio of Item Price to Invoice Amount.
For example, if the Invoice Amount was USD 2000.00 and the Total Net and Gross Mass where 100.000 and 150.000 respectively, on setting the Item Price to USD 200.00, the item level Net and Gross Mass would automatically be set to 10% of the totals, so 10.000 and 15.000 respectively.
Total Gross Mass will be included in the declared data but Total Net Mass is not supported by the CDS system.
Box 31 - Containers
DE 7/10 - Container identification number
Containers can be declared at header level (where they apply to all the goods on the declaration) or at item level, where a container relates to a specific item.
Containers are in a grid.
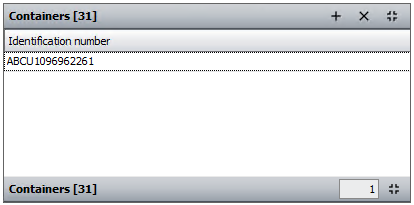
Enter the container identification number, if the goods will be in a container at the point of entering the EU.
If the container numbers are not yet known (for example on a pre-lodged declaration), then enter numbers unknown.
If the exact details are not available when the declaration is lodged, the details must be entered later. This can be done prior to arrival at the frontier using standard amendment procedures. If not containerised or it’s not known whether they are containerised then leave blank.
Notes
The term container covers:
- large, re-usable containers, for example, ISO types designed to be transported by road, rail, sea, or air
- smaller re-usable types of containers of an internal volume of a cubic metre or more designed to be transported by road, rail, sea or air and capable of specialised handling without unloading
- specialised re-usable containers designed to be used for the particular goods and transported by road, rail, sea or air
- goods are to be regarded as containerised even when a container is mounted on a road vehicle or rail wagon
If you enter container numbers here, Sequoia will automatically declare Box 19 - Container to indicate that the goods are containerised.
Box 31 - Goods Description
DE 6/8 - Description of goods
Description of goods is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
Enter a description of the goods which is specific enough to allow the unambiguous identification, classification and examination of goods.
This description can be up to 512 characters long. Where the commodity code depends on size, weight or other physical criteria, the description should include that information.
If you declare a CUS Code in box 31 for chemical substances and preparations, a precise description of the goods may be waived.
For goods removed from a customs warehouse or an excise warehouse the relevant stock numbers must be included.
For excise goods, a full description of the goods including container sizes and strength etc. must always be provided.
Box 31 - Packages
DE 6/9 - Type of packages
DE 6/10 - Number of packages
DE 6/11 - Shipping marks
Packages are declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
Each package declaration consists of 3 components as follows:
Type of Packages
DE 6/9 - Type of packages
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required package type.
The package type code of the smallest external packing unit is to be declared in accordance with UN/ECE recommendation 21.
The smallest external packaging is defined as being the one in which the goods are packaged in such a way that they cannot be divided without first undoing the packing.
A list of package type codes can also be found [here].
Number of Packages
DE 6/10 - Number of packages
Enter the number of packages (of the type declared above) or for unpacked goods, the number of pieces.
For bulk goods:
- When goods are imported as loose bulk (for example, grain or oil) enter 1.
- For bulk consignments made through a fixed energy installation, enter 0.
- For break bulk consignments (for example timber,cars), enter the number of separately (packaged) units (for example, bundles or each car).
Shipping Marks
DE 6/11 - Shipping marks
Enter a free text description of any marks and numbers on transport units or packages.
Where there is one common identifying number for all of the packaging then only this number need be entered. For unpackaged goods, enter ‘Unpackaged’.
For bulk traffic, enter ‘Loose Bulk’ or ‘Break Bulk’.
Box 31 - CUS Code
DE 6/13 - CUS code
The CUS code is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
Where the goods concerned are subject to a TARIC measure in relation to a CUS code, the CUS code must be provided. The provision of the CUS code is optional where no TARIC measure exists for the goods concerned.
Chemicals classified in chapters 28 and 29 of the UK Trade Tariff should be described (in box 31 - Goods Description) using their precise chemical name and the appropriate 8-digit CUS reference number declared here.
The CUS (Customs Union and Statistics) number is the identification number assigned to chemical products in the European Customs Inventory of Chemical Substances (ECICS) database.
Where the chemical is not listed, the precise name in accordance with British Standard 2474/1983 and the words ‘not listed’ must be declared in box 31 - Goods Description.
Box 33 - Commodity Code
DE 6/14 - Commodity code – Combined Nomenclature code
DE 6/15 - Commodity code – TARIC code
Commodity codes in CDS declarations are the same as they were in CHIEF. Whilst technically the Combined Nomenclature code (the first 8 digits) and the TARIC code (digits 9 and 10) have separate data element numbers, for imports they form a single, 10 digit commodity code.
The commodity code is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
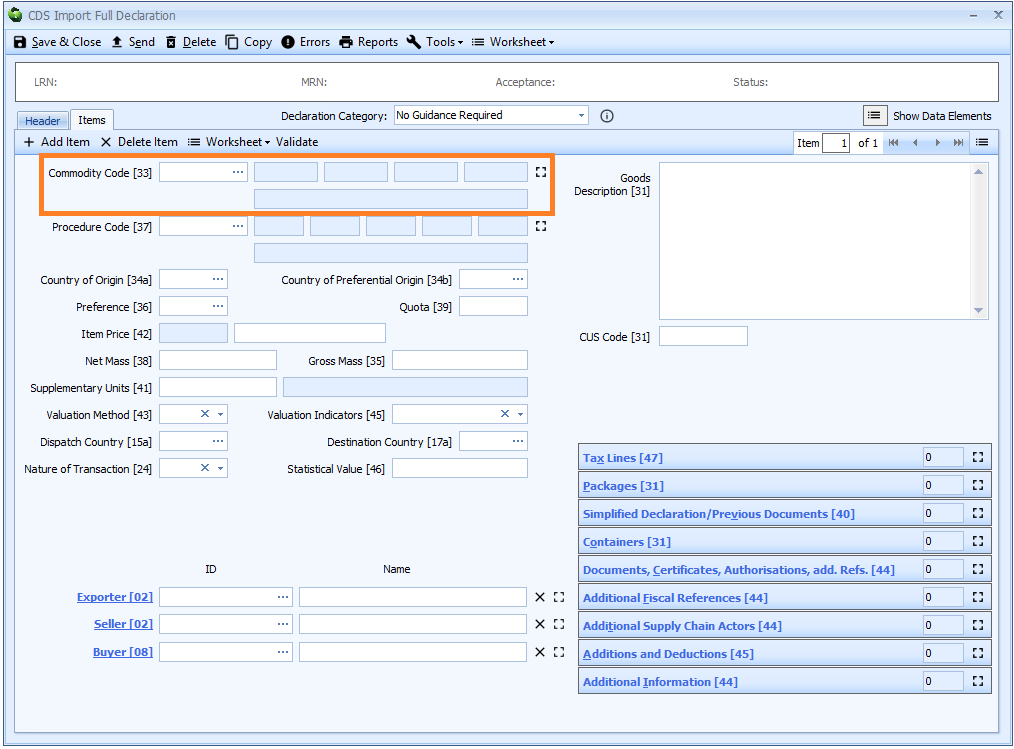
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display the customs tariff, from which you can select the required commodity code.
This is exactly the same as it was for CHIEF declarations. The Sequoia customs tariff browser is shown below.
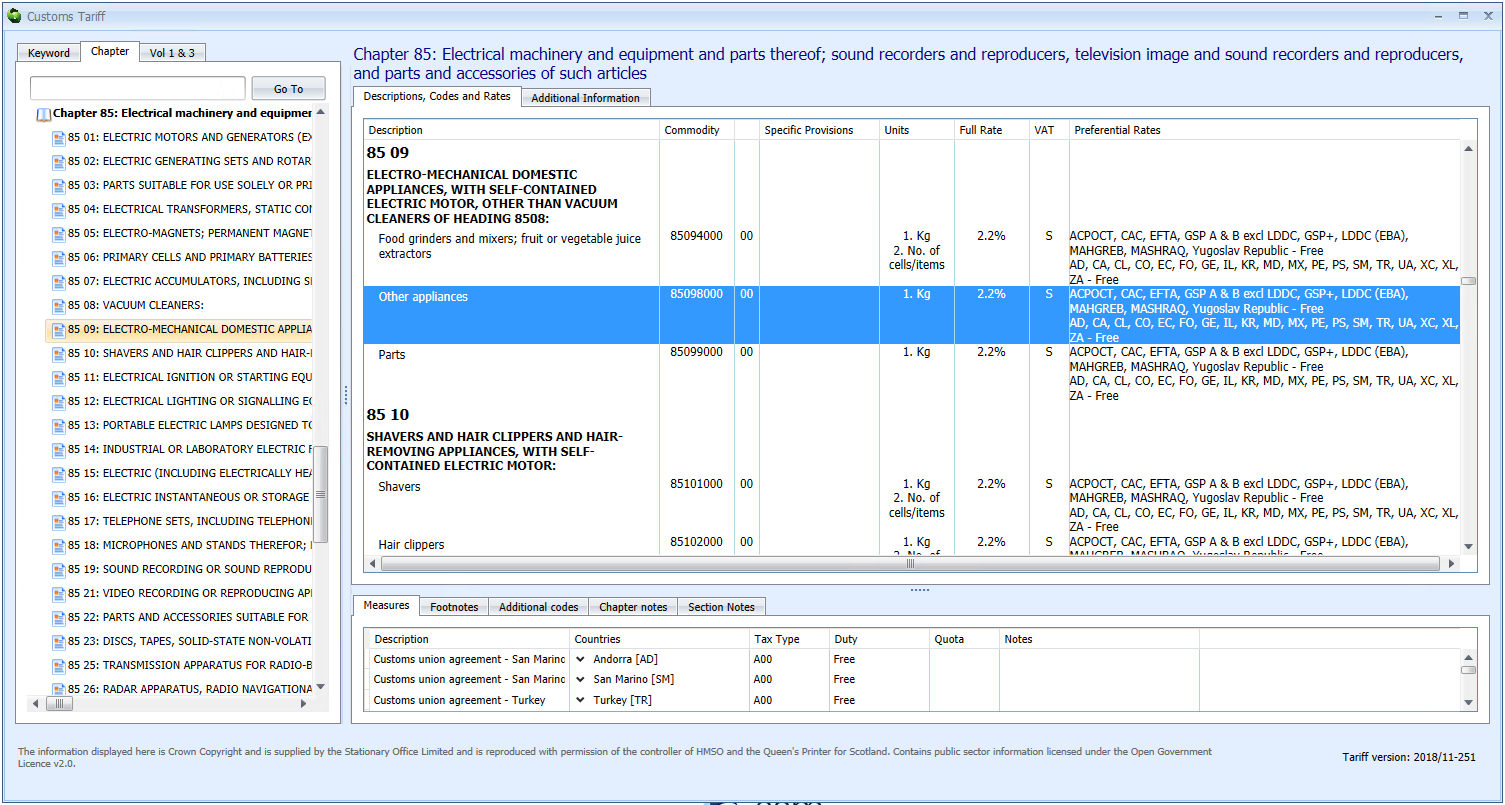
You can also look up commodity codes, duty and VAT rates here.
The real change in CDS is how additional commodity codes are declared (see below).
Additional Commodity Codes
DE 6/16 - Commodity code – TARIC additional code(s)
DE 6/17 - Commodity code – National additional code(s)
Whilst the legislation differentiates between TARIC and national additional codes, now that we have left the EU this difference is irrelevant. HMRC have however retained most or all of the EU defined codes.
Each item in a declaration to CDS can have up to 99 additional commodity codes. The image below shows how (some of) these are displayed in Sequoia.
Only 4 additional codes are visible by default. In most circumstances that should be more than enough (hopefully!). They are all disabled until you have entered the main commodity code.
Once you do that the first additional code is enabled. If you enter that then the second one is enabled, and so on.
If, in the unlikely event that you need to enter more than 4 additional commodity codes, you can click the ![]() expand icon to the right of the last additional code box to display a grid, into which you can add more.
expand icon to the right of the last additional code box to display a grid, into which you can add more.
In CDS, these commodity additional codes not only allow you to declare any anti-dumping and/or countervailing duty applicable to the goods.
They are also used to declare excise duty types and to claim zero rating for VAT (such as on children's clothing) for instance. In CDS they are a fundamental part of the way revenue is calculated.
On CHIEF declarations those were declared on tax lines in box 47. That is not the case for CDS.
You can find a list on gov.uk for the following:
You can find information on and guidance on selecting the correct commodity and additional commodity codes, including details of any additional codes which may apply in the Sequoia tariff or in the UK trade tariff.
Box 34a - Country of Origin
DE 5/15 - Country of origin code
The country of origin is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
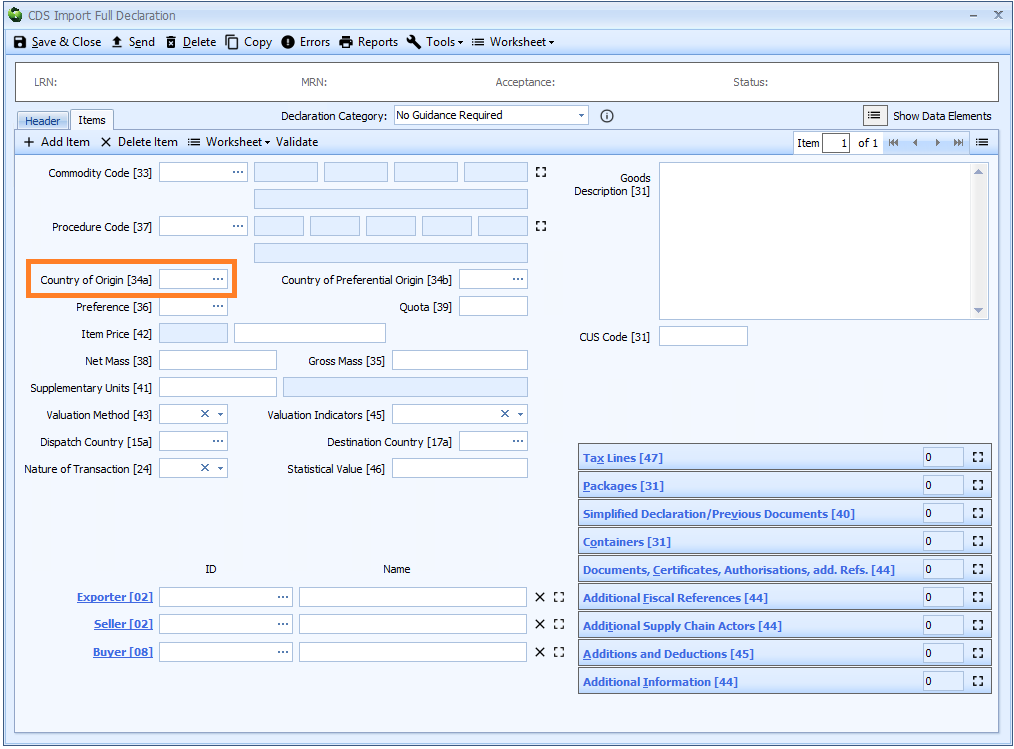
The country of origin is mandatory if the preference code entered in box 36 begins with 1 (i.e. you are not claiming preference).
If you are claiming preferential treatment then you will have to complete Box 34b - Country of Preferential Origin.
In those circumstances, this box (34a) is only required if the country of non-preferential origin is different to the country of preferential origin.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required country code.
A list of country codes is also available [here].
Box 34b - Country of Preferential Origin
DE 5/15 - Country of preferential origin code
The country of preferential origin is mandatory if you are claiming preference - i.e. the preference code entered in box 36 does not begin with 1.
This can be a country code or potentially a country group code.
The country of preferential origin is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
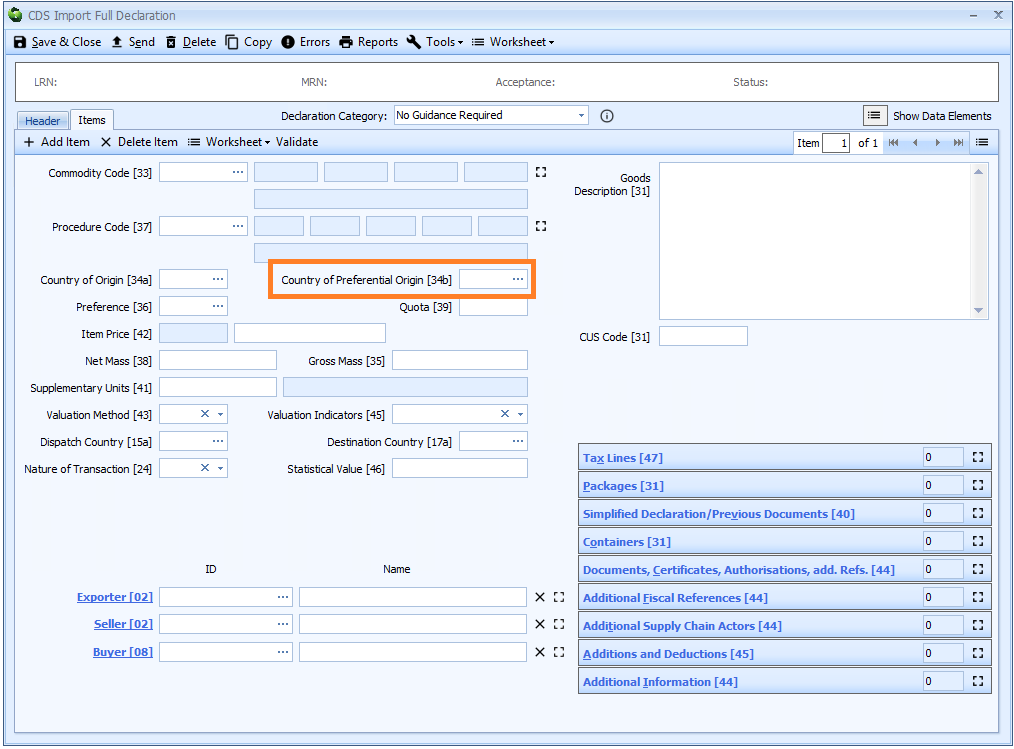
You can enter the code into the box or enter a ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog
from which you can select the required country code.
The country of preferential origin is only required on a simplified declaration where controlled goods are being entered.
It may be left blank for goods entered to a customs warehouse. However, where preferential origin status is being claimed at the time the goods are entered to a customs warehouse,
the preference claim is indicated on the simplified declaration through the use of an AI statement code in box 44 of WHSRP.
A list of country codes is available here and a list of country group codes is also available [here].
Box 35 - Gross Mass
DE 6/5 - Gross mass (kg)
Gross mass is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
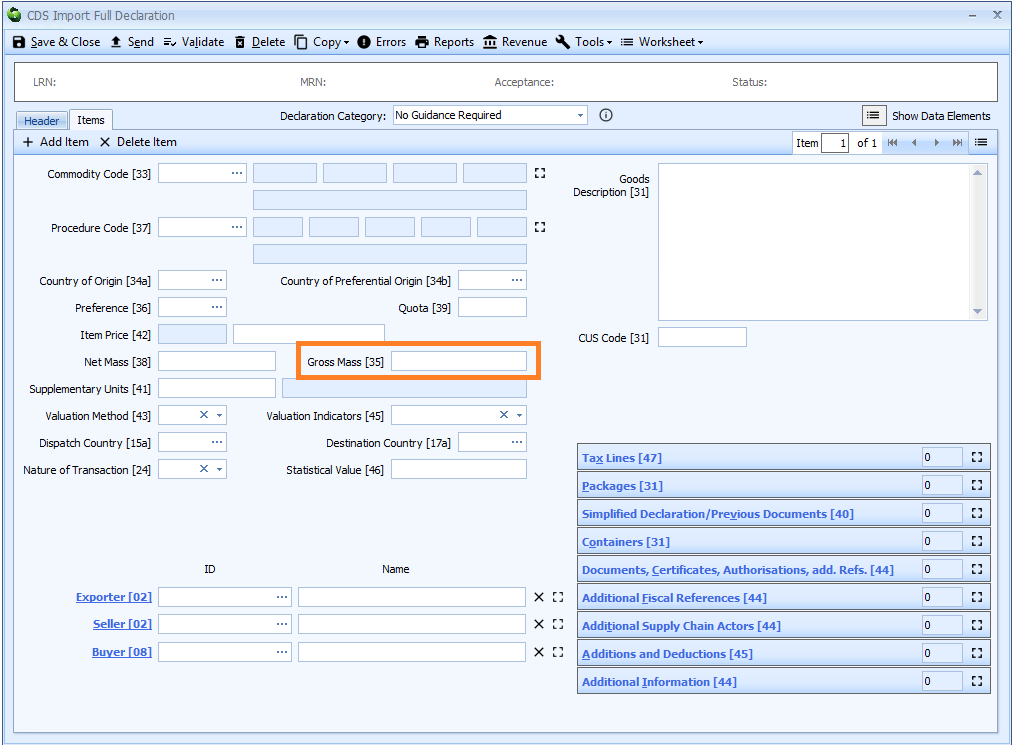
Also refer to Total Net Mass and Total Gross Mass.
Enter the gross mass in kilograms.
The gross mass is the total weight of the goods and packaging but excluding containers and any other transport equipment.
Where a gross mass greater than 1 kg includes a fraction of a unit (kg), it may be rounded off in the following manner:
- From 0.001 to 0.499: rounding down to the nearest kg,
- From 0.5 to 0.999: rounding up to the nearest kg.
A gross mass of less than 1 kg should be entered as ‘0’ followed by a number of decimals up to 6, discarding all ‘0’ at the end of the quantity (for example 0.123 for a package of 123 grams, 0.00304 for a package of 3 grams and 40 milligrams or. 0.000654 for a package of 654 milligrams).
The gross mass can be up to 16 digits of which up to 6 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 4 decimal places, you can only have up to 12 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Box 36 - Preference
DE 4/17 - Preference
Preference is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
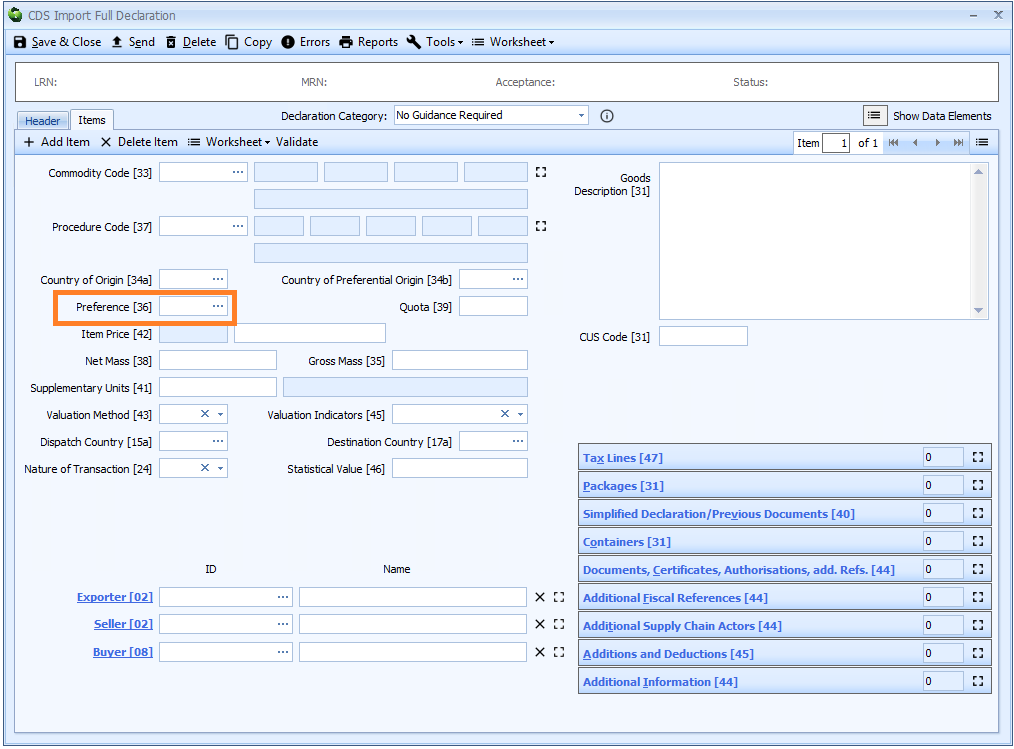
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required preference code.
A preference code is mandatory for all imports where the goods are:
- entering a free circulation regime (including end use)
- where a claim to tariff preference or quotas is established upon entry to the customs procedure
The 3-digit code indicates whether a reduction in, or relief from, import duty applies. This includes specific duties and other equivalent charges applicable to CAP goods.
A list of preference codes is also available [here].
Box 37 - Procedure Code
DE 1/10 - Procedure
The procedure code is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
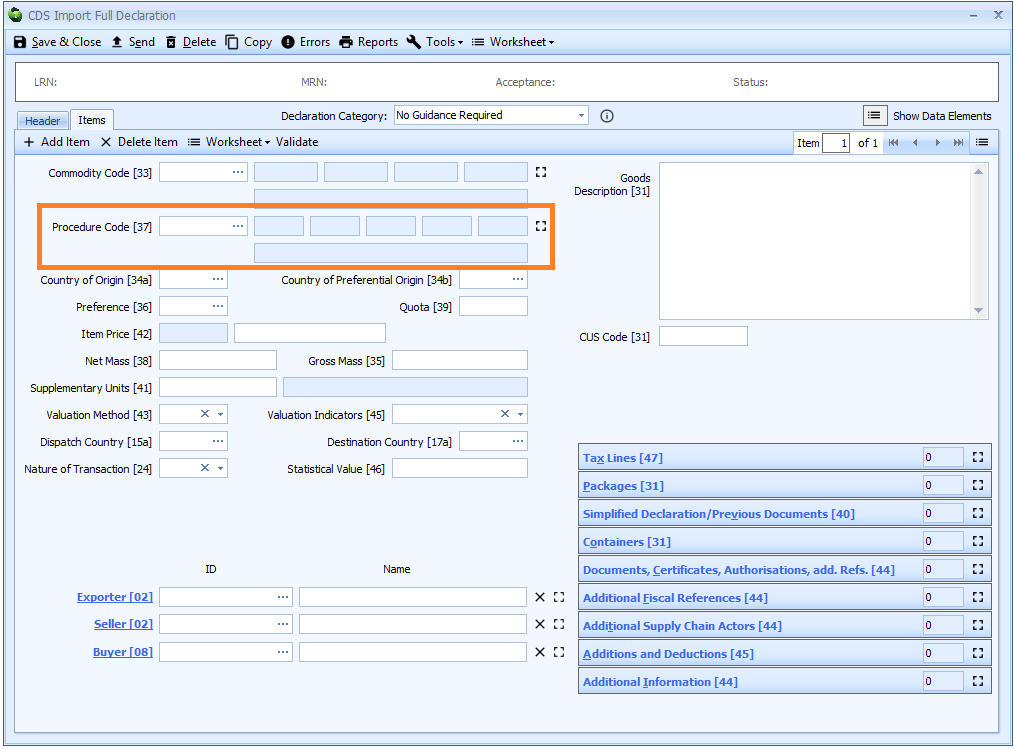
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required procedure code.
The procedure code is essentially the first 4 digits of the old CHIEF CPC code.
-
The first 2 digits are the Requested Procedure; the customs procedure to which the goods are being entered.
-
The third and fourth digits are the Previous Procedure; the customs procedure from which the goods are being removed (
00indicates that the goods have not been subject to any previous procedure).
This is essentially the same as it was for CHIEF declarations, although some codes have been removed/changed.
A multi-item declaration on CDS can only include requested procedure codes for the same declaration category.
A list of requested and previous procedure codes is available [here].
Additional Procedure Codes
DE 1/11 - Additional procedure
A big change in CDS is how additional procedure codes are declared.
As soon as you enter the procedure code - as above - the first additional procedure code box is enabled (as shown below).
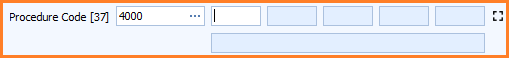
Each item in a declaration to CDS can have up to 99 additional procedure codes.
Only 5 additional codes are visible by default. In most circumstances that should be more than enough (hopefully!). They are all disabled until you have entered the main commodity code.
Once you do that the first additional code is enabled. If you enter that then the second one is enabled, and so on.
If, in the unlikely event that you need to enter more than 5 additional procedure codes, you can click the ![]() expand icon
to the right of the last additional code box to display a grid, into which you can add more.
expand icon
to the right of the last additional code box to display a grid, into which you can add more.
To specify that there are no additional procedure codes, enter 000.
In CDS, these additional codes replace some of the tax line functionality in CHIEF.
In CHIEF there were several specific CPC codes - for example:
- 4000 C07 - to claim relief from customs duty and VAT for goods with an intrinsic value not exceeding £15
where you had to specify details in box 47 for the correct duty (A00) and VAT (B00) tax rates and method of payment in order to claim the relief. If you didn't specify the correct information then the declaration would be rejected and an error message generated.
In CDS in normal circumstances you do not need to declare tax lines in box 47. Instead you have to declare additional procedure codes - (C07 and F45) in the above example - to claim relief.
If you don't declare the codes, then any reliefs to which they relate will not be granted, but the declaration would still be accepted and no error message would be generated.
Lists of additional procedure codes can also be found [here].
Box 38 - Net Mass
Net mass is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
The net mass can be up to 16 digits of which up to 6 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 4 decimal places, you can only have up to 12 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Also refer to Total Net Mass and Total Gross Mass.
Box 39 - Quota
DE 8/1 - Quota order number
Enter the 6 digit order number of the tariff quota, if applicable.
This is only required on a simplified declaration where a claim to a tariff quota is being made on that simplified declaration.
Quota is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
Box 40 - Simplified Declaration-Previous Documents
DE 2/1 - Simplified Declaration/Previous Documents
Previous documents can be declared at header level (where they apply to all the goods on the declaration) or for each item.
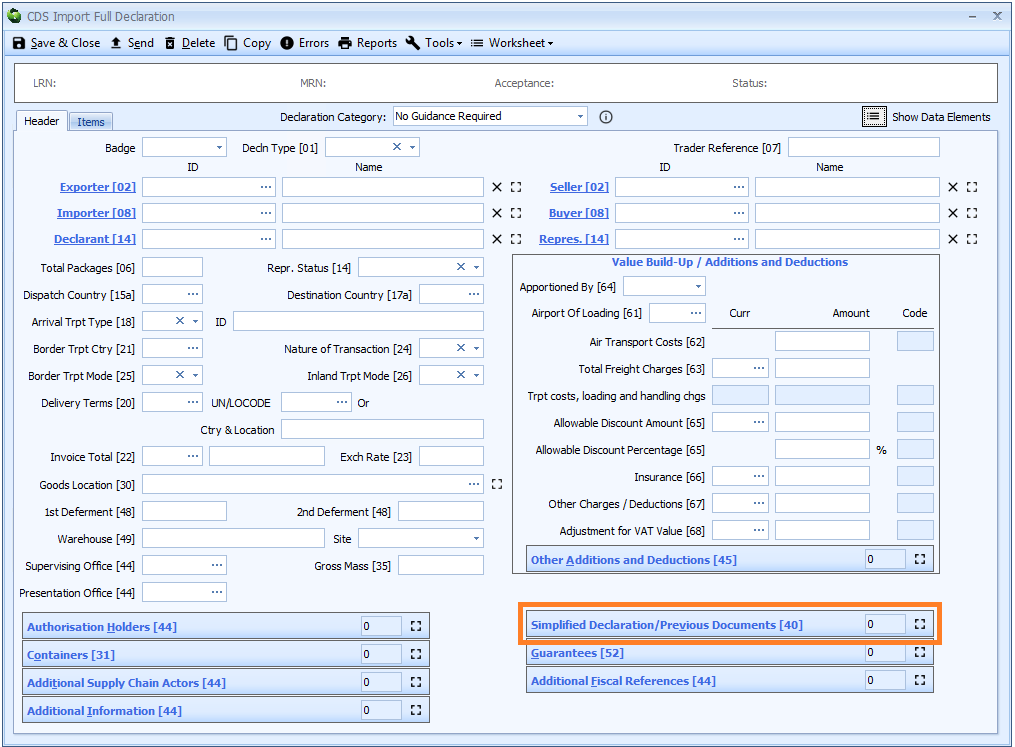
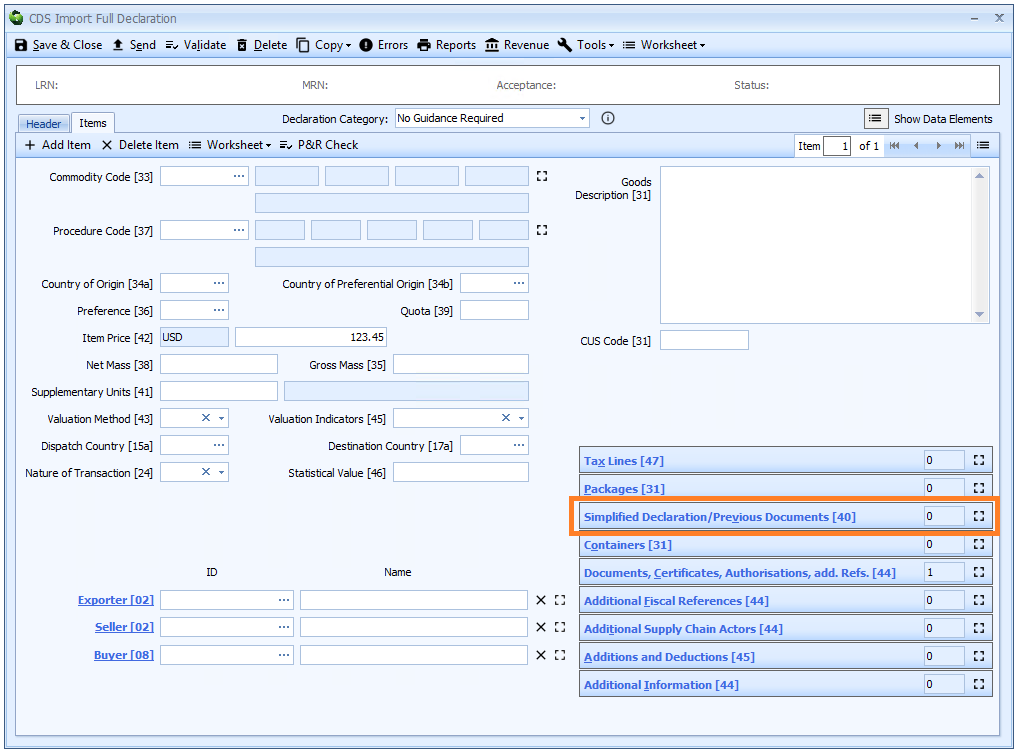
They are displayed in a grid.
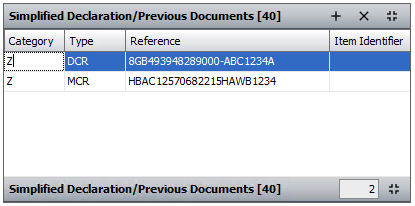
CDS declarations include both the MUCR and DUCR as previous documents (as shown in the above example), as well as any associated DUCR part number. CHIEF had these as separate boxes.
Sequoia will automatically enter the DUCR (and MUCR as appropriate) as previous documents for you.
Simplified declaration/previous documents have 4 components, as described below.
Document Category
A category is always required and must be one of the following:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| X | Declaration for temporary storage |
| Y | Simplified declaration or the entry in the declarant’s records |
| Z | Previous document |
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required category.
Document Type
A document type is always required.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required document type.
A list of previous document codes can also be found [here].
Document Reference
Enter the identifying reference number for the document.
Goods Item Identifier
The fourth component is used to identify which item of the previous document is being referred to; the goods item number on the summary declaration, temporary storage declaration, simplified declaration, entry in records or other previous document.
Where the previous document referred to contained only a single goods item, this component may be left blank.
Box 41 - Supplementary Units
DE 6/2 - Supplementary Units
Supplementary Units are declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
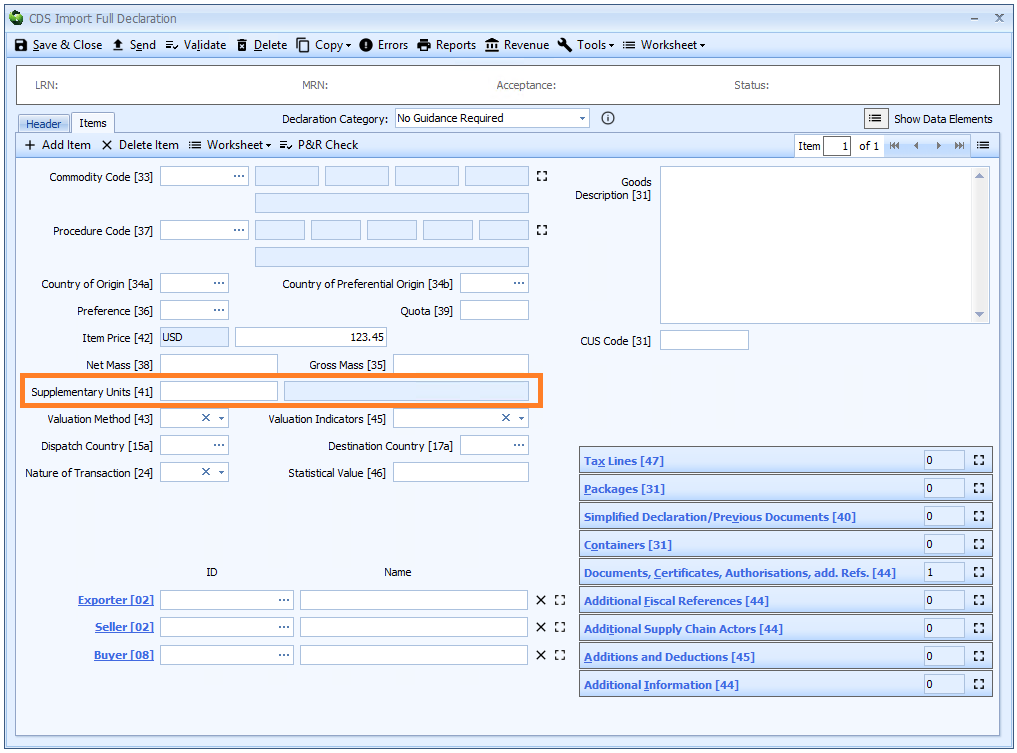
Supplementary units are only required where the commodity code specifies a supplementary unit.
In the online UK Trade Tariff, any supplementary unit required to be declared is indicated where a 'Supplementary unit' measure (column 2) is shown under the 'Import' or 'Export' tab (as illustrated below).
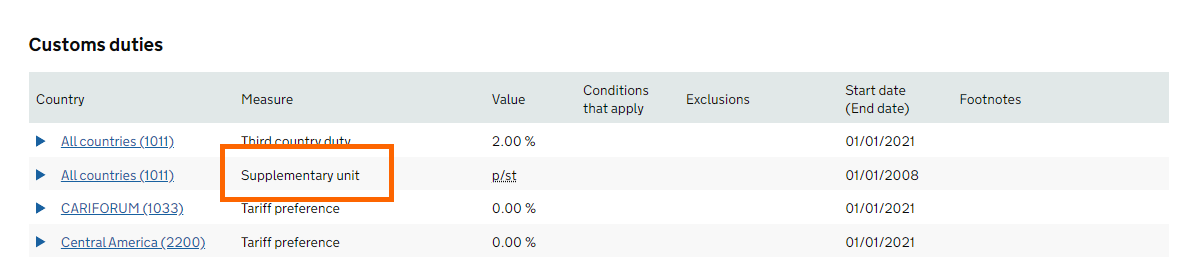
Supplementary units can be up to 16 digits of which up to 6 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 4 decimal places, you can only have up to 12 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
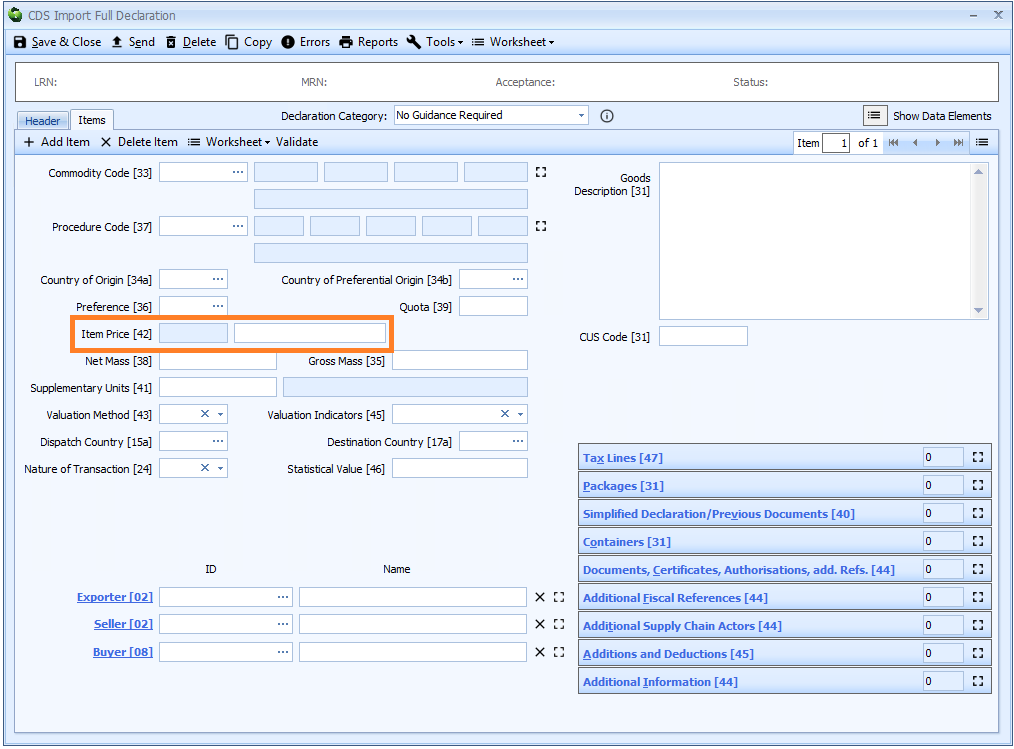
Box 42 - Item Price
DE 4/14 - Item price/amount
The item price is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
In most cases, you must enter the invoice price. However:
Where Valuation Method 1 or 6 is being used for Customs Duty purposes,
-
the invoice price must be adjusted to include any addition or deduction allowable from a purchase price which is not shown in box 45 - Additions and Deductions.
In such cases, the item value must be calculated manually and the net amount entered here. Document code
9WKSmust be declared in box 44 - Documents Certificates Authorisations and Additional References.
When the invoice price/value being declared is duty inclusive (box 20 - Delivery terms of DDP),
-
the total invoice amount must include any Customs Duty (including any secured duty), definitive anti-dumping duty, definitive countervailing duty and retaliatory duty.
The amount of customs duties to be deducted from the item price must be declared in box 45 - Additions and Deductions using code
BC.
Item price is only required on a simplified declaration where:
- controlled goods are being entered, or
- a claim to a tariff quota is being made.
Box 43 - Valuation Method
DE 4/16 - Valuation method
The valuation method must be completed for all items on the declaration to indicate the valuation method to be used to calculate the value for Customs Duty.
The valuation method is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
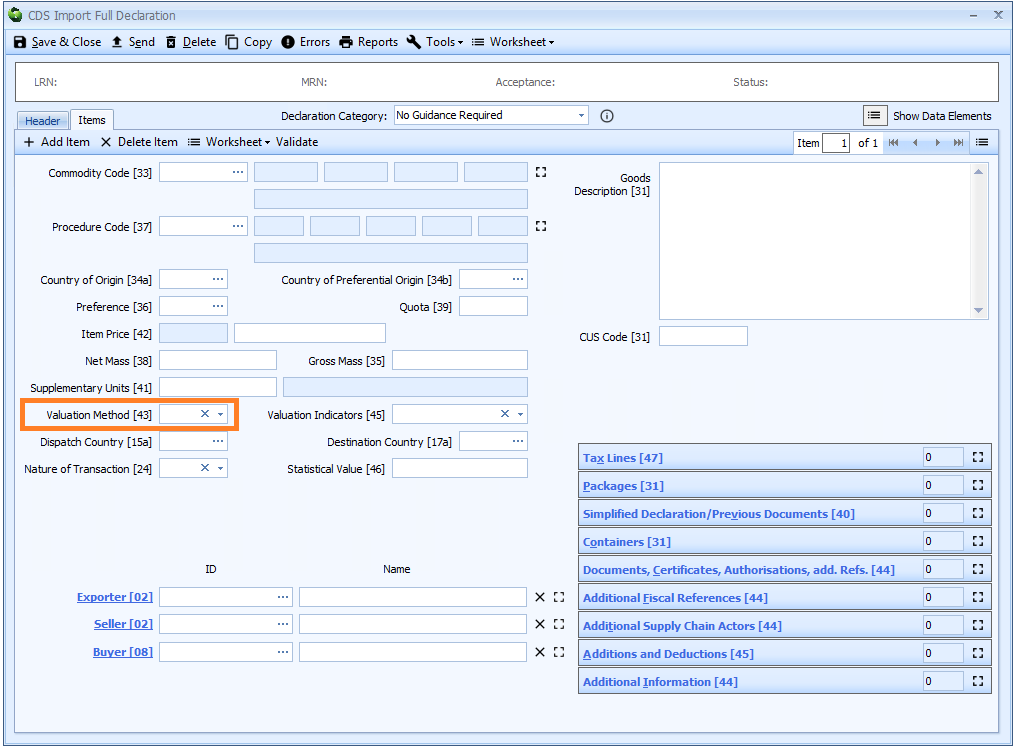
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Transaction value of the goods |
| 2 | Transaction value of identical goods |
| 3 | Transaction value of similar goods |
| 4 | The Deductive Method |
| 5 | The Computed Value Method |
| 6 | The ‘Fallback’ Method |
The valuation method is only required on a simplified declaration where a claim to a tariff quota is being made on that simplified declaration.
Box 44 - Documents Certificates Authorisations and Additional References
DE 2/3 - Documents produced, certificates and authorisations, additional references
Documents are declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
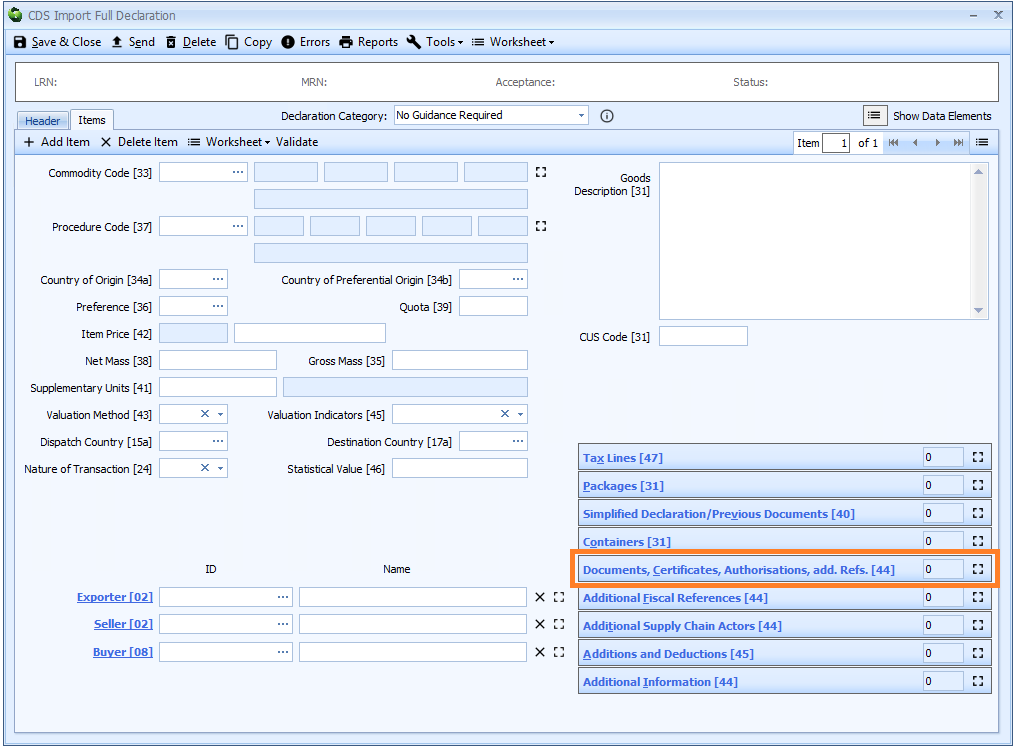
They are displayed in a grid.
The information required is split into several components:
Type
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required document type.
A list of Documents and other reference codes is also available [here].
You should also refer to the procedure code guidance for information on which Document Codes should be used in order to use specific customs procedures.
Status
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required document status.
Not all document type codes require you to declare the status. You should refer to Appendix 5 - list of document and other reference codes for information on the requirements.
A list of document status codes is available [here].
Reference
You should refer to Appendix 5 - list of document and other reference codes for information on which reference, if any, is required for a specific document type.
To indicate a specific line of a document (some licences for instance cover many products with each defined as a line), you need to add the line number to the end of the document reference, separated by
-(a dash).For example, to declare the fourth line of document reference 'X23994' you would declare
X23994-4in the reference box.
Units
A measurement unit is normally a 3 character code but some codes have a single character suffix (a 'qualifier').
For example,
KGMis the code for kilograms, whereas kilogram gross isKGMG.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
Measurement units are only required if you are also declaring the quantity (see below). They are only required where a specific quantity and measurement type has to be decremented against a specific document (e.g. a licence has been issued for a total quantity of liquids in litres).
Where this is the case, enter the appropriate code for the commodity’s/document’s measurement unit type using the list provided in appendix 20 - Measurement unit codes.
The above list of measurement unit codes on gov.uk also provides a cross reference to the codes used on CHIEF.
Quantity
Enter the quantity being attributed to the specific document.
The quantity can be up to 16 digits of which up to 6 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 4 decimal places, you can only have up to 12 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
If you are declaring the quantity then you will also need to declare the units (see above).
Validity Date
The date of validity, if required, must be entered in the following date format yyyymmdd
For Licences and non-preference certificates:
- The date to be declared is the expiry date for the licence or certificate. Where the Document Code for the licence or certificate is listed in Appendix 5C - Document and other reference codes: Licence types, a date of validity must always be declared.
For Preferential proofs of origin (e.g. EUR1, GSP, Invoice Declarations, Statements of Origin):
- The date to be declared is the date of issue. This is conditional on the specific document codes completion notes.
Issuing Authority
Where required, enter a free text description of the Issuing Authority. This should be specific enough to identify the governing body responsible for issuing the licence or certificate.
Reason
Where required, enter a free text description of the reason.
Box 44 - Additional Information
DE 2/2 - Additional information
Additional information can be declared at header or item level, depending on the code used.
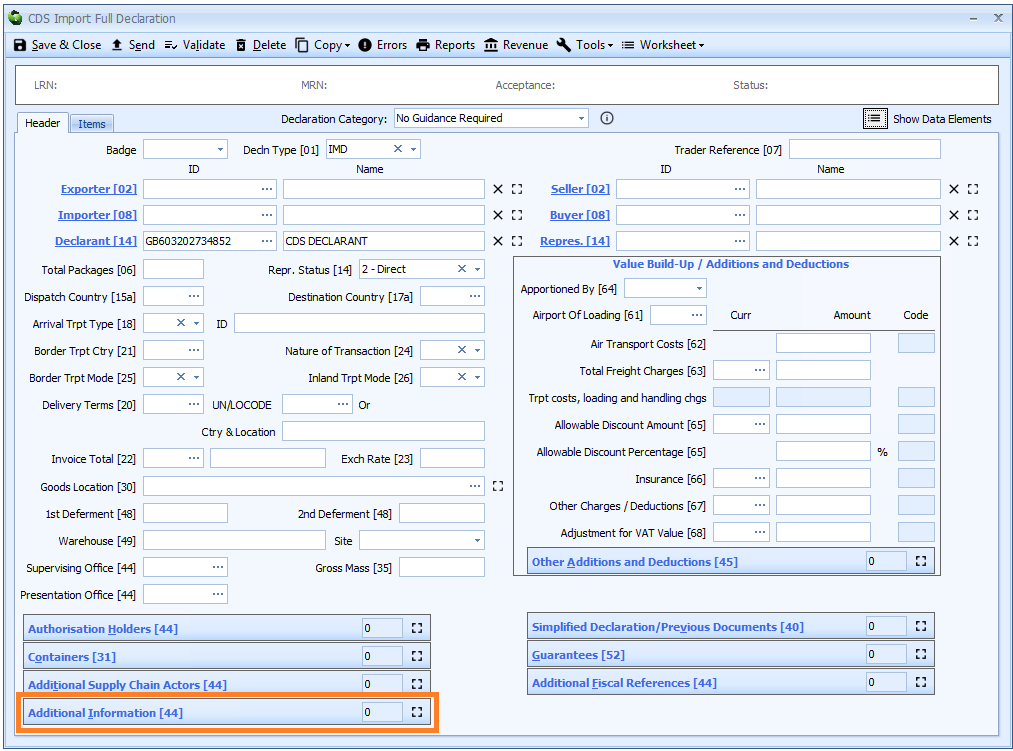
Additional information where required consists of a code and, in certain circumstances, free text information.
See Appendix 4 - Additional information (AI) statement codes for CDS for information on which codes require a description to be entered and what the description should be (see the 'Details to be entered on the declaration or clearance request' column).
Box 44 - Supervising Office
DE 5/27 - Supervising customs office
The supervising office only to be completed when specifically instructed by the completion notes for the Procedure Code. These notes also indicate which supervising office is to be declared.
Supervising customs office is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
In most circumstances this would be a UK supervising office.
Codes for supervising offices in other member states can be found in The EU's customs office list.
Box 44 - Office of Presentation
DE 5/26 - Customs office of presentation
Presentation customs office is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
This data element is only required where a SASP authorisation is used to release the goods. It is made up of two components.
For all SASP declarations the code should use one of the following formats:
For goods presented in the UK
Enter the appropriate code from Appendix 17 - List of UK supervising offices on gov.uk.
For goods presented in other member states
Codes for supervising offices in other member states can be found in The EU's customs office list.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
Box 44 - Authorisation Holders
DE 3/39 - Holder of the authorisation
Authorisation holders are declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
Authorisation holders are only mandatory where an authorisation is required to declare the goods.
The Procedure Code and Additional Procedure Code completion notes give guidance on the Authorisation Type Codes expected to be used in specific circumstances for the procedure concerned.
An authorisation holder declaration is typically required if:
- A deferment number is used to defer the payment of customs duty
- Goods are being declared to a special procedure (such as IP or customs warehousing) and an authorisation number is quoted in box 44 - Documents Certificates Authorisations and Additional References.
There are two components as follows:
Authorisation Type Code
A 3 or 4 character code is required for each Authorisation Holder declared.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of authorisation type codes can also be found in Appendix 6.
Identifier
Enter the EORI number of the authorised party.
Box 44 - Additional Supply Chain Actors
DE 3/37 - Additional supply chain actor(s)
An additional supply chain actor is declared on the header tab of the declaration form if it is the same for all the goods on the declaration, otherwise it must be declared for each item on the item tab.
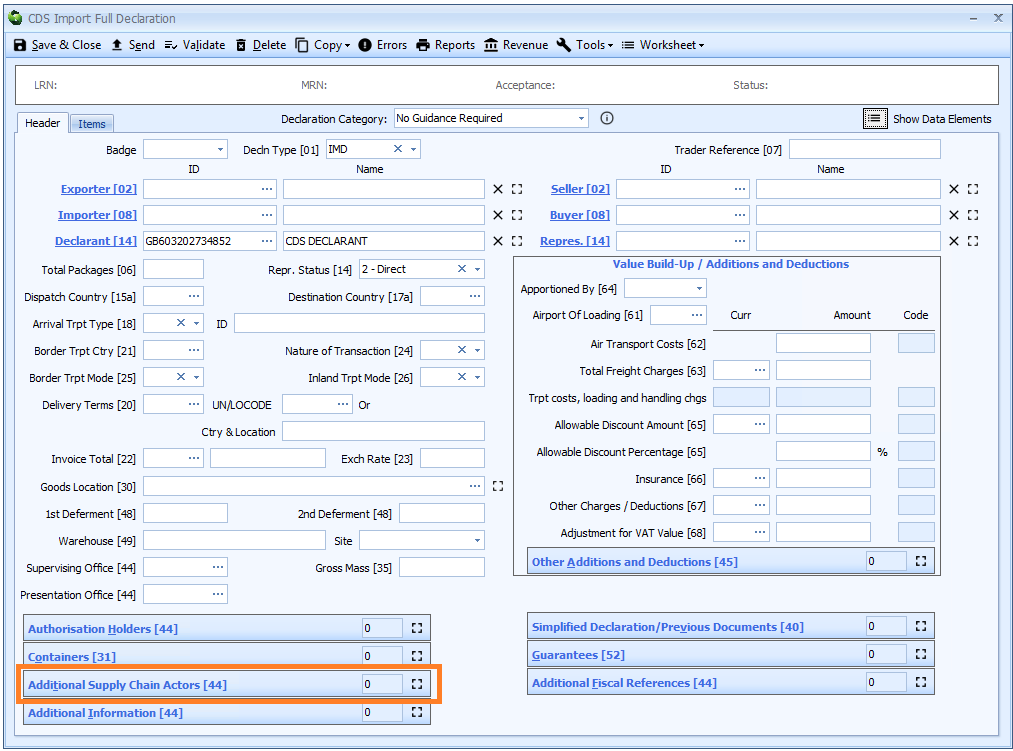
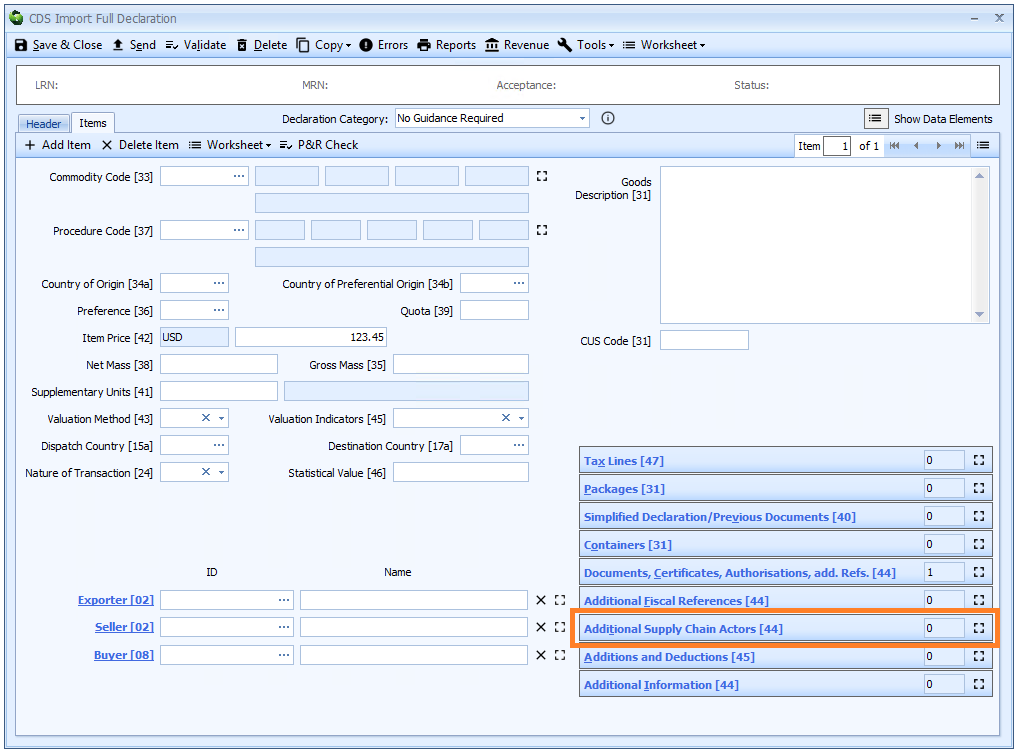
Declaring Additional Supply Chain Actors is optional.
There are two components as follows:
Role Code
A code is required for each Additional Supply Chain Actor declared.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
| Role code | Party | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CS | Consolidator | Freight forwarder combining individual smaller consignments into a single larger consignment (in a consolidation process) that is sent to a counterpart who mirrors the consolidator’s activity by dividing the consolidated consignment into its original components |
| MF | Manufacturer | Party which manufactures goods |
| FW | Freight Forwarder | Party undertaking forwarding of goods |
| WH | Warehouse Keeper | Party taking responsibility for goods entered into a warehouse |
Identification number of the party
This should be either:
- an EORI number issued by a Member state, or;
- a unique identification number assigned to an economic operator of a third country in the framework of a trade partnership programme developed in accordance with the World Customs Organisation Framework of Standards to Secure and Facilitate Global Trade which is recognised by the European Union.
Box 44 - Additional Fiscal References
DE 3/40 - Additional fiscal references
Additional fiscal references are declared on the header tab of the declaration form (where they apply to all the goods on the declaration) or at item level..
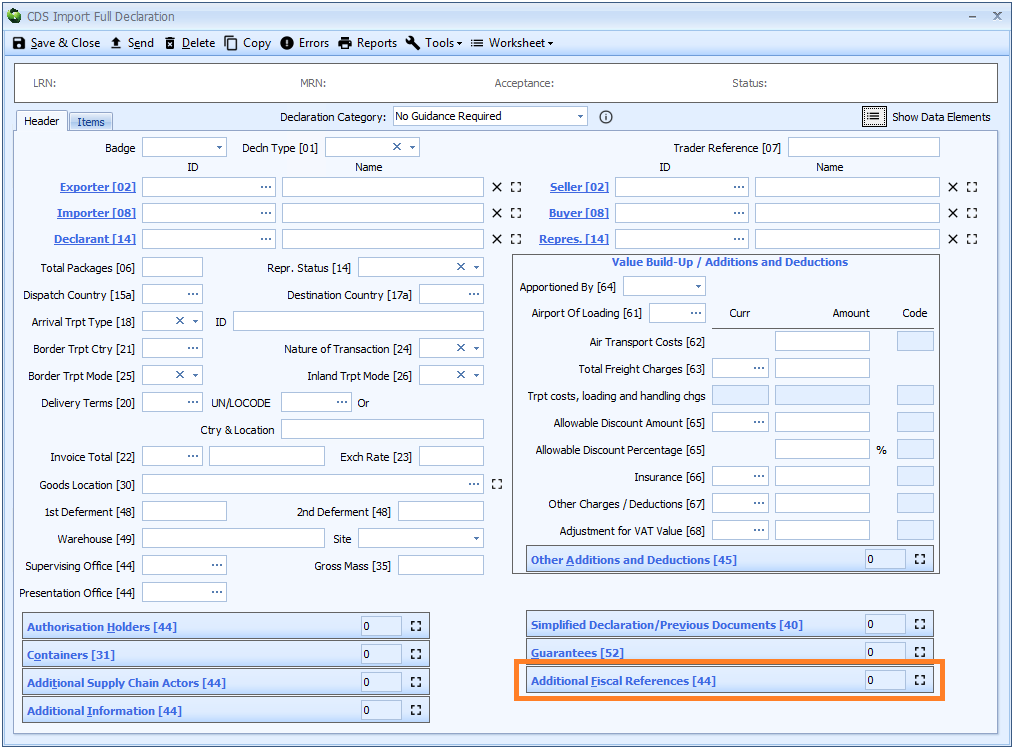
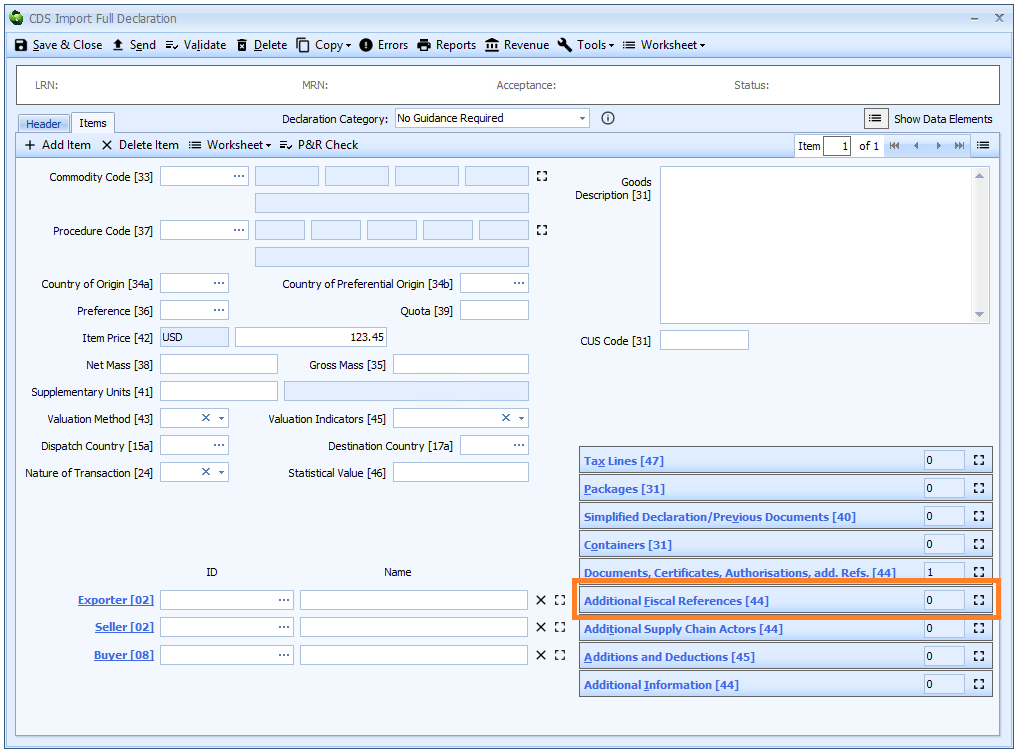
Additional Fiscal References must be completed when Onward Supply Relief (OSR) is claimed. They are only required when Requested Procedure Code 42 is used in box 37.
An Additional Fiscal Reference must also be declared - at header level - when any VAT due is being accounted for by Postponed VAT Accounting (PVA).
There are two components as follows (both of which are required):
Role Code
A code is required for each Additional Fiscal Reference declared.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
| Role code | Party | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FR1 | Importer | Enter the VAT identification number issued in the member state of importation for the importer designated or recognised under Article 201(1) of the VAT Directive as liable for payment of VAT. FR1 should be used for an importer that is established and VAT registered in the UK, it cannot be used by a non-VAT registered person. FR1 should be declared for Postponed VAT Accounting (PVA) and the importer's details declared as the VAT identification number |
| FR2 | Customer | Enter the VAT identification number of the customer who is liable for the VAT on the intra-community acquisition of goods in accordance with Article 200(1) of the VAT Directive. FR2 should be used for the customer in the member state where the goods are going to, it cannot be used by a non-VAT registered person. |
| FR3 | Tax Representative | Enter the VAT identification number issued in the member state of importation for the tax representative. FR3 should be used for a UK VAT registered/established agent appointed to act as an importer by a trader who is not established, and VAT registered in the UK. The appointed agent/importer will be treated as importing and supplying the goods as the principal - see section 2.7 and 2.8 of VAT Notice 702: imports for the UK agent tax responsibilities, it cannot be used by a non VAT registered person. |
| FR4 | Holder of the deferred payment authorisation | The taxable person or the person liable for payment or another person that has received deferment of payment in accordance with Article 211 of Directive 2006/112/EC. |
VAT identification number
The value added tax identification number is structured as follows:
- Country Code of the member state of issue, followed by;
- the Individual number attributed by member states for the identification of taxable persons referred to in Article 214 of Directive 2006/112/EC (for example, the individual’s VAT number).
Box 45 - Valuation Indicators
DE 4/13 - Valuation indicators
Valuation indicators are declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
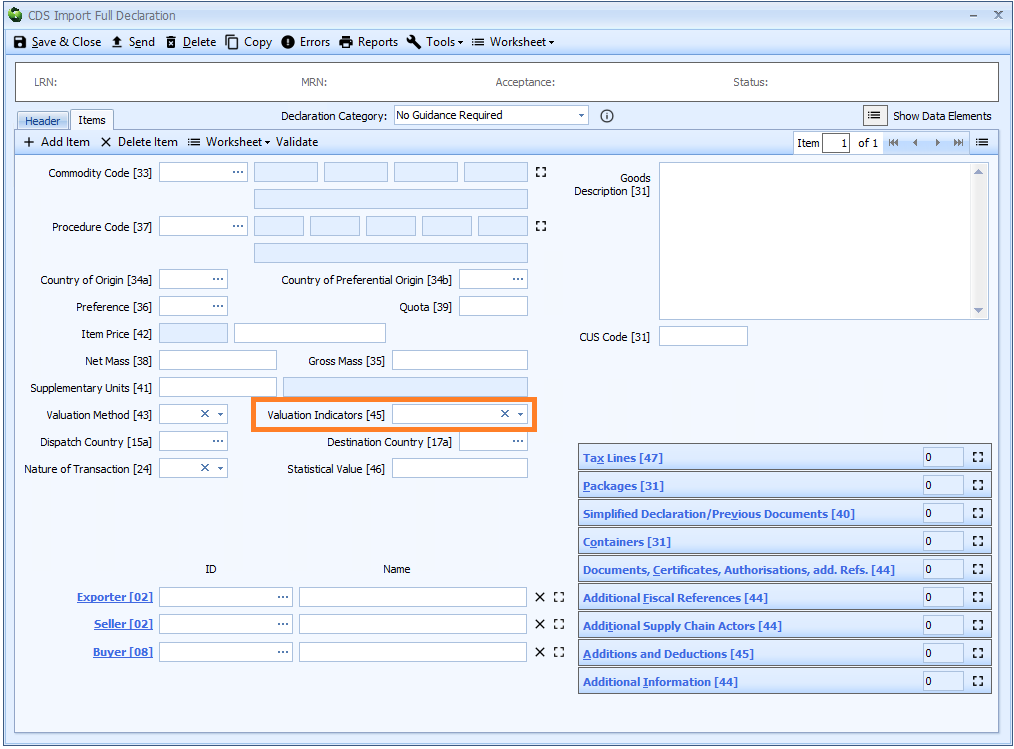
Valuation indicators are required for declarations using Valuation Method 1 - the transaction value of the goods. Otherwise they should be left blank.
Valuation indicators are a 4 digit code, representing the answers to the 4 questions - as listed below. The answer to each question is represented as either 1 for yes or 0 for no.
| Digit | Question | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Is there is a price influence as a result of a Party Relationship between the buyer and seller? | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | Are there any restrictions as to the disposal or use of the goods by the buyer in accordance with Article 70(3)(a) of the UCC? | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | Is the sale or price subject to some condition or consideration in accordance with Article 70(3)(b) of the UCC? | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | Is the sale subject to an arrangement under which part of the proceeds of any subsequent resale, disposal or use accrues directly or indirectly to the seller? | 1 | 0 |
For example, if the answer to the first question above is yes, but the answer to the other questions is no then the code to declare would be 1000.
Valuation indicators must be completed for importations to Inward Processing when the declarant opts to use the Article 86(3) customs debt rules as laid down in the UCC..
Valuation indicators must not be completed for goods which have been entered under Simplified Procedure Value (SPV) and Standard Import Value (SIV). It cannot therefore be used with Additional Procedure Code
E01orE02in box 37.
Box 45 - Additions and Deductions
DE 4/9 - Additions and deductions
Additions and deductions are amounts that are required to be added to or deducted from the item price of the goods to arrive at the value for customs purposes.
Prior to the UCC these are values that would have been declared on form C105A. They can be declared at header and/or item level.
Additions and deductions must not be completed for goods which have been entered under Simplified Procedure Value (SPV) and Standard Import Value (SIV).
They cannot therefore be used with Additional Procedure CodeE01orE02in box 37 - Additional Procedure Code.
Most additions and deductions are entered in a grid but at header level some additional codes have been added by HMRC to reflect the 'value build up' - VBU - boxes used in CHIEF (boxes 61 to 68). Therefore the header page of CDS declarations in Sequoia displays additions and deductions differently - as illustrated below.
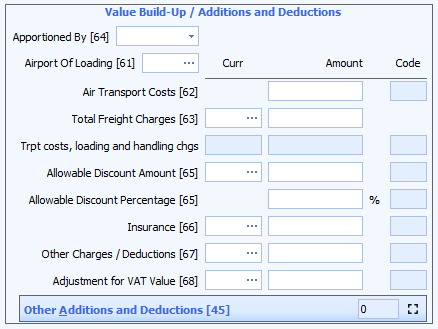
Additions and Deductions have the following components:
Apportioned by (header level VBU only)
For these header level 'value build up' boxes (61 to 68) as above, Sequoia will automatically fill in the 'code' required. However in some cases (e.g. air transport costs), the code depends on whether the value is to be apportioned across the items by value or gross mass.
Enter the mode of apportionment as follows:
- Value
- Gross mass
You can select this from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Airport of Loading (header level VBU only)
The airport of loading is required if you are declaring air transport costs in box 62.
You can enter the airport code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
Where the goods were shipped from an airport not listed in Appendix 15b - Airport codes, the code for the nearest listed airport must be used.
For consignments transhipped via another member state, the airport of loading for the journey to the EU (the third country airport) should be declared rather than the EU airport of transhipment.
You can find a list of allowable airport codes in Appendix 15b (which includes the percentage and indicates which zone the airport is in).
Only that percentage of the air transport costs are included in the calculation of the value for customs duty.
Code
Codes that apply to:
- Additions begin with an
A - Deductions begin with a
B.
For header level 'value build up' boxes the code will be filled in automatically once you enter an amount or percentage.
For other additions and deductions at header level and all additions and deductions at item level you will have to specify the code that applies.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of allowable codes can be found in Appendix 10.
Currency
Where there is a currency box to the left of the amount you must enter the currency code.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
Amount or percentage
Enter the amount or percentage that applies.
Box 46 - Statistical Value
DE 8/6 - Statistical value
Statistical value is declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
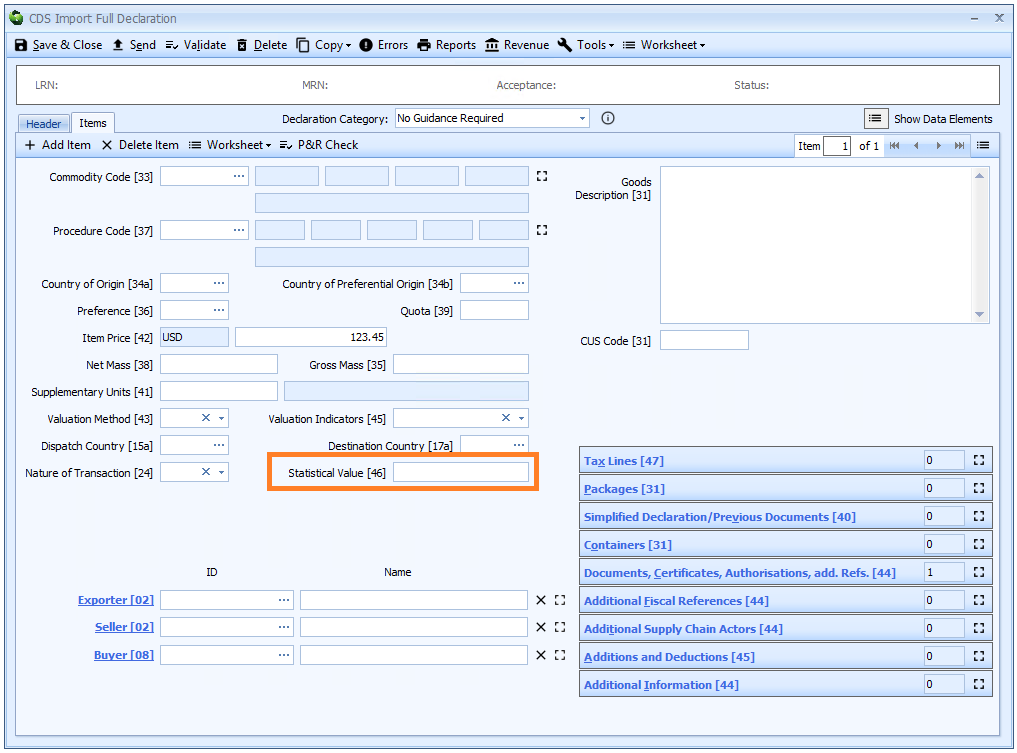
Where required, enter the statistical value for the goods item in GBP (£ sterling), irrespective of the currency used for the Invoice Total or Item Price.
You should refer to the procedure code completion notes to identify when the statistical value is required.
The statistical value can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 2 digits may be after the decimal point.
I.e. if you have 2 decimal places, you can only have up to 14 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Box 47 - Tax Lines
DE 4/3 - Calculation of taxes – Tax type
DE 4/4 - Calculation of taxes – Tax base
DE 4/5 - Calculation of taxes – Tax rate
DE 4/6 - Calculation of taxes – Payable tax amount
DE 4/7 - Calculation of taxes – Total
DE 4/8 - Calculation of taxes – Method of payment
In normal circumstances, you don't have to enter tax lines when making declarations to CDS.
Any revenue due is calculated automatically using information from elsewhere in the declaration (i.e. commodity code, procedure code, preference etc.).
However, if you need to declare taxline information, this is split into several components as detailed below.
Tax lines are declared on the item tab of the declaration form.
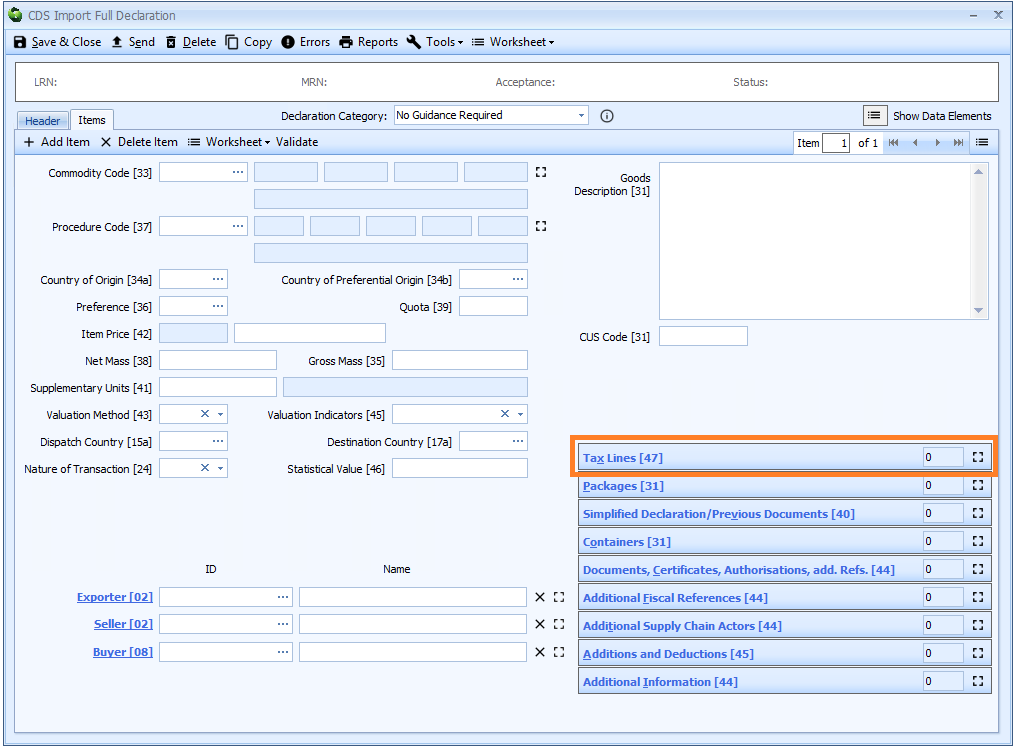
Generally, the only reason to declare any tax line information is if you are calculating the amount of revenue due manually, as required by the Procedure Code you are using. In those circumstances, you will also need to declare a box 44 - Additional Information statement with a code of
OVR01.
Tax Type
DE 4/3 - Calculation of taxes – Tax type
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of allowable tax types is also available in Appendix 8.
Method of Payment
DE 4/8 - Calculation of taxes – Method of payment
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of Method of payment codes can also be found in Appendix 9.
Tax Base
DE 4/4 - Calculation of taxes – Tax base
Generally, the only reason to declare a tax base is if you are calculating the amount of revenue due manually, as required by the Procedure Code you are using. In those circumstances, you will also need to declare a box 44 - Additional Information statement with a code of
OVR01.
Tax Base Quantity and Measurement Unit
This should be completed where a measurement unit and qualifier (as applicable) are required to support the calculation of the tax amount; for example a third quantity is required such as alcoholic strength by volume.
Where a commodity code needs a measurement unit and qualifier (where applicable), this will be specified against the commodity code details in Volume 2 of the UK Trade Tariff.
Measurement Unit
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of allowable measurement unit codes is also available in Appendix 20.
Quantity
Enter the quantity as per the measurement unit above.
The quantity can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 6 digits may be after the decimal point. I.e. if you have 6 decimal places, you can only have up to 10 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Tax Base Amount and Currency
This should be completed where a value is required to support the calculation of the tax amount, as specified in the Procedure Codes completion rules.
Currency
In normal circumstances, this should be GBP.
You can enter the code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
A list of currency codes can also be found in Appendix 11.
Amount
Enter the required amount.
The amount can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 2 digits may be after the decimal point. I.e. if you have 2 decimal places, you can only have up to 14 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Tax Rate
DE 4/5 - Calculation of taxes – Tax rate
The HMRC import declaration completion guidance suggests that this is only ever required on a C21 declaration.
Payable Tax Amount
DE 4/6 - Calculation of taxes – Payable tax amount
When a manual tax calculation is required, the payable tax amount should be completed showing the amount of revenue (in GBP) to be paid or secured for each tax type.
The amount can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 2 digits may be after the decimal point. I.e. if you have 2 decimal places, you can only have up to 14 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Total
DE 4/7 - Calculation of taxes – Total
When a manual tax calculation is required, the total tax should be completed showing total amount of revenue to be paid or secured for the tax type.
The amount can be up to 16 digits, of which up to 2 digits may be after the decimal point. I.e. if you have 2 decimal places, you can only have up to 14 digits before the decimal point. If you have no decimal places, you can have up to 16 digits before the decimal point.
Box 48 - Deferment Numbers
DE 2/6 - Deferred payment
Deferment numbers are declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
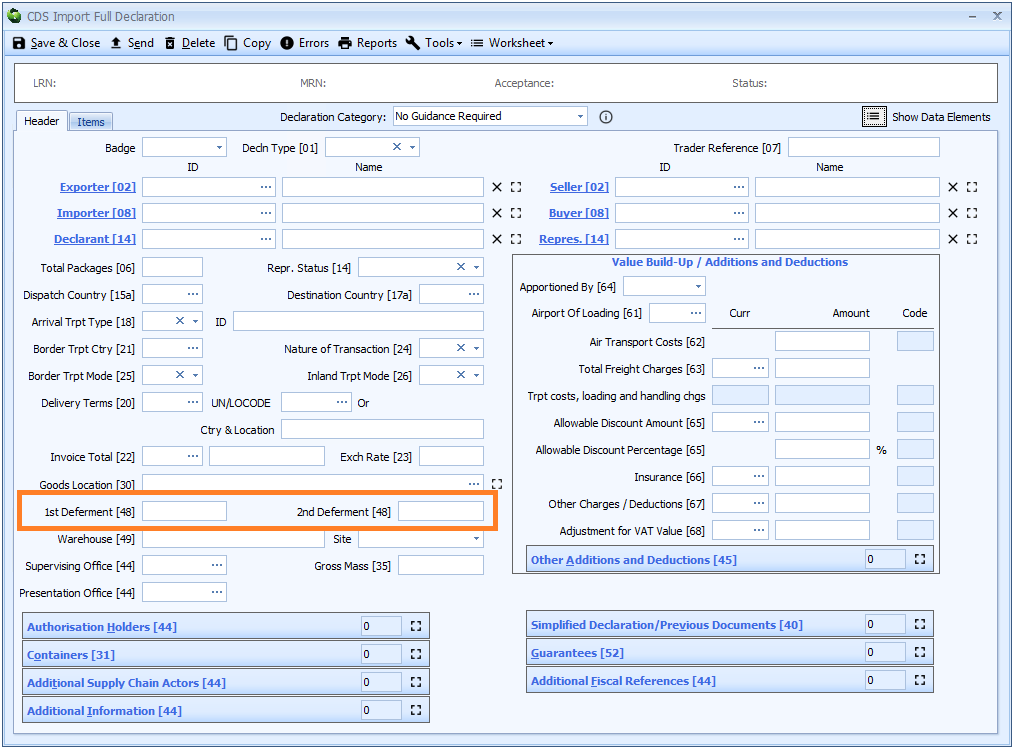
CDS import declarations can accept one or two deferment numbers, in the same way as CHIEF does. No prefix is required; only the 7 digit number(s).
If two deferment numbers are declared, they cannot be the same number. There is no restriction on which deferment number is declared as first or second.
Revenue is allocated against these deferment accounts as follows:
| Deferment | Revenue |
|---|---|
| Only one | All revenue is deferred to this account |
| Two | VAT is deferred to second deferment account. All other revenue is deferred to the first account. |
When a deferment is used to defer the payment of customs duty, you also have to declare details as follows:
- Document codes
C505(or505N) andC506in box 44 - Documents Certificates Authorisations and Additional References - Authorisation Holder types
DPOandCGUin box 44 - Authorisation Holders
Box 49 - Warehouse
DE 2/7 - Identification of warehouse
This is only required when box 37 - requested or previous procedure code, or both
includes the codes 07, 71 or 78 or where goods are removed from a warehouse and are declared using a procedure code in the 61 series.
Identification of warehouse is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
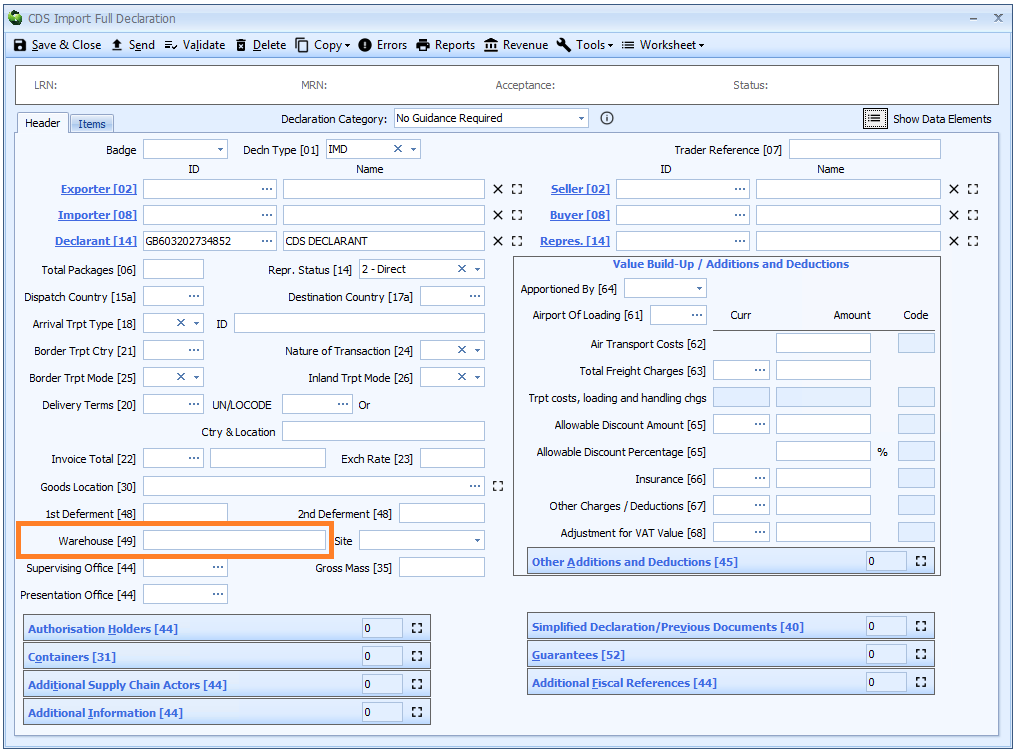
In Sequoia, the warehouse is declared as a single reference, combining both the warehouse type code and the identifier - e.g. R1234567GB.
The warehouse code has 2 components as follows:
Warehouse type
| Code | Warehouse type |
|---|---|
| R | Public customs warehouse type I |
| S | Public customs warehouse type II* |
| T | Public customs warehouse type III* |
| U | Private customs warehouse |
| Y | Non-customs warehouse |
| Z | Free zone |
* Type codes S and T may not be used with any warehouse identifier with a Country Code of GB.
Warehouse Identifier (including Country Code)
The warehouse identifier consists of 2 parts:
- the identification number for the warehouse issued by the authorising member state (including the warehouse type as the first character)
- the Country Code for the authorising member state
In the UK:
- customs warehouses have a 7-digit reference - e.g.
R1234567GB - excise warehouses have a 13-character reference - e.g.
YGB00001234567GB - the Free Zone is
0000006- Isle of Man
If the warehouse identity is not a UK allocated code (suffixed by GB), the premises name and address must be supplied as an AI Statement in box 44 Additional Information, using AI code PREMS.
Separate declarations are required for goods destined for/removed from different warehouses. The Procedure Code notes explain these restrictions in more detail.
Warehouse Site
This site code is used in Sequoia if you are using the Customs Warehousing module for duty management functionality. It is not transmitted as part of the declaration.
You can type the code directly into the box or select from the drop-down list using the ![]() icon to the right of the box.
icon to the right of the box.
Warehouse sites are configured in the Sequoia Management Console application. They relate to physical locations within a single warehouse authorisation.
Box 52 - Guarantees
DE 8/2 - Guarantee type
DE 8/3 - Guarantee reference
The guarantee is declared on the header tab of the declaration form.
Whilst the legislation states that you can declare up to 9 instances of Guarantee Type and 99 instances of guarantee reference for each type, in CDS you are restricted to 99 guarantees in total. In reality that should be more than you ever need (most likely only one)!
A guarantee is typically required if:
- A deferment number is used to defer the payment of customs duty, or;
- A cash account is being used to pay customs duty, or;
- Goods are being declared to a special procedure (such as IP or customs warehousing).
A guarantee is only required on a simplified declaration where a claim to a critical tariff quota is being made on the simplified declaration.
A guarantee is made up of the following components:
Guarantee Type
DE 8/2 - Guarantee type
You can enter the Guarantee Type code into the box or enter ? - a question mark - into the box to display a lookup dialog from which you can select the required code.
The Guarantee Type codes that you can enter are as per the list below.
| Description | Code |
|---|---|
| For guarantee waiver (Article 95(2) of the Code) | 0 |
| For comprehensive guarantee (Article 89(5) of the Code | 1 |
| For individual guarantee in the form of an undertaking by a guarantor (Article 92(1)(b) of the Code) | 2 |
| For individual guarantee in cash or other means of payment recognised by the customs authorities as being equivalent to a cash deposit, made in euro or in the currency of the member state in which the guarantee is required (Article 92(1)(a) of the Code | 3 |
| For individual guarantee in the form of vouchers (Article 92(1)(b) of the Code and Article 160) | 4 |
| For guarantee waiver where the amount of import or export duty to be secured does not exceed the statistical value threshold for declarations laid down in accordance with Article 3(4) of Regulation (EC) No 471/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (15) (Article 89(9) of the Code) | 5 |
| For individual guarantee in another form which provides equivalent assurance that the amount of import or export duty corresponding to the customs debt and other charges will be paid (Article 92(1)(c) of the Code) | 7 |
| For guarantee not required for certain public bodies (Article 89(7) of the Code) | 8 |
| For guarantee furnished for goods dispatched under TIR procedure | B |
| For guarantee not required for goods carried by fix transport installations (Article 89(8)(b) of the Code) | C |
| For guarantee not required for goods placed under the temporary admission procedure in accordance with Article 81(a) of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446 (Article 89(8)(c) of the Code) | D |
| For guarantee not required for goods placed under the temporary admission procedure in accordance with Article 81(a) of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446 (Article 89(8)(c) of the Code) | E |
| For guarantee not required for goods placed under the temporary admission procedure in accordance with Article 81(c) of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446 (Article 89(8)(c) of the Code) | F |
| For guarantee not required for goods placed under the temporary admission procedure in accordance with Article 81(d) of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446 (Article 89(8)(c) of the Code) | G |
| For guarantee not required for goods placed under the Union transit procedure in accordance with Article 89(8)(d) of the Code | H |
| Cash Accounts (to be used for payment or security purposes) | Y |
Guarantee Reference
DE 8/3 - Guarantee reference
Where:
- document code
C505is declared in box 44 - Documents Certificates Authorisations and Additional References and ; - authorisation type code
CGUis declared in box 44 - Authorisation Holders,
then the comprehensive guarantee reference number must be declared here.
Where revenue is being paid/secured by means of a cash account, enter the EORI number of the holder of the Cash Account being used to pay/secure any duties and charges where codes N or P are declared in box 47 - Method of payment.
A guarantee reference is only required on a simplified declaration where a claim to a critical tariff quota is being made on the simplified declaration.
Other Guarantee Reference
The use of this component and the circumstances in which it should be declared, whilst supported in a CDS declaration, has not been defined by HMRC!
Access Code
The use of this component and the circumstances in which it should be declared, whilst supported in a CDS declaration, has not been defined by HMRC!
Currency
The use of this component and the circumstances in which it should be declared, whilst supported in a CDS declaration, has not been defined by HMRC!
Amount
The use of this component and the circumstances in which it should be declared, whilst supported in a CDS declaration, has not been defined by HMRC!
Office of Guarantee
The use of this component and the circumstances in which it should be declared, whilst supported in a CDS declaration, has not been defined by HMRC!
CDS Import Declarations Screenshots
CDS Import Full Declaration Header Page
CDS Import Full Declaration Items Page
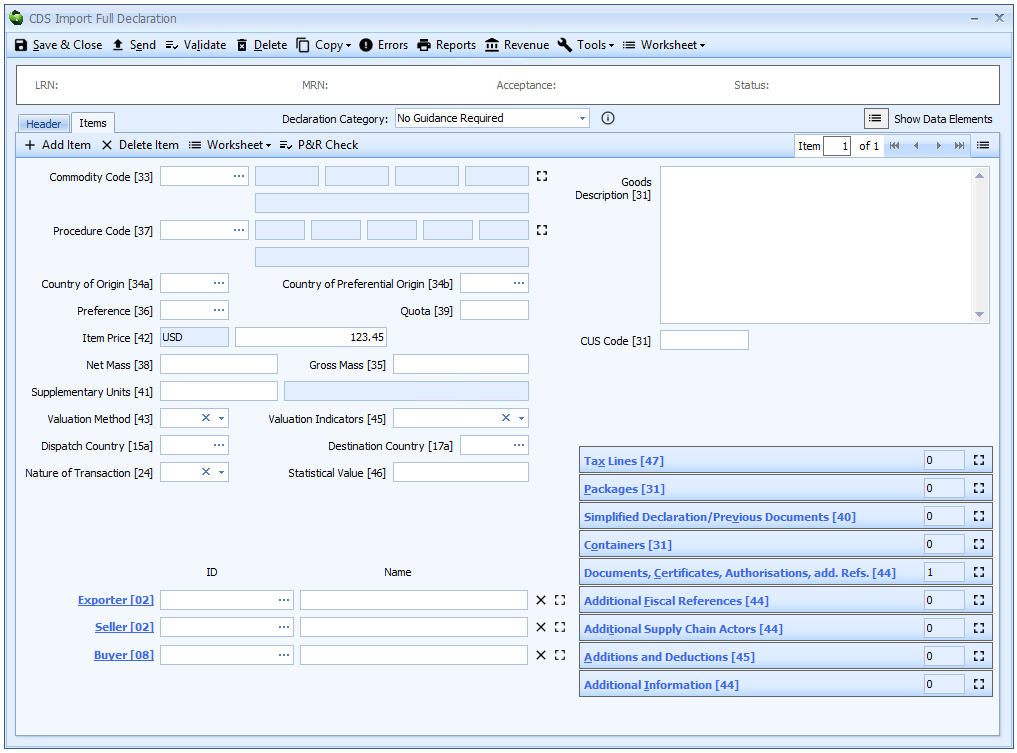
CDS Import Simplified Declaration Header Page
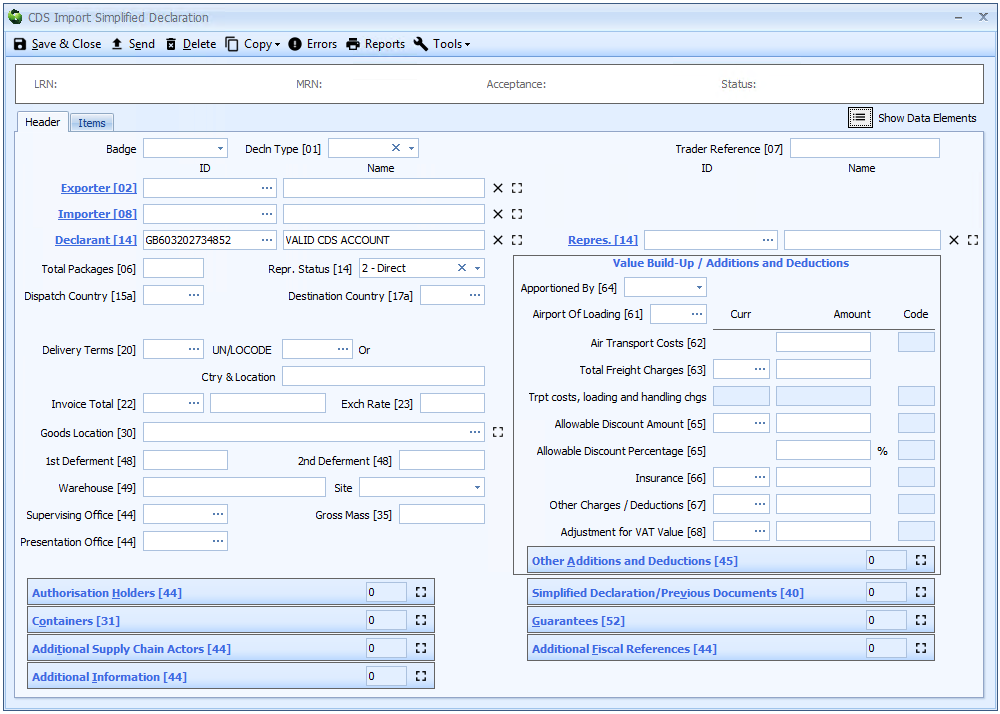
CDS Import Simplified Declaration Items Page
CDS Import C21 Declaration
CDS Import C21 EIDR Declaration